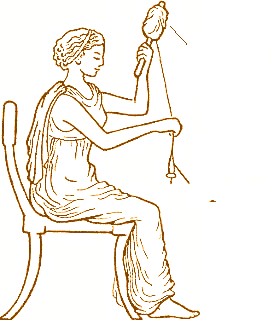
I’m not sure what the Three Kings were doing on the day after Epiphany. But, the shepherds, if they were like medieval English farmworkers, would still be on holiday. They went back to work, traditionally, next Monday, which is Plough Monday – (See my post here). This year, January 12th. By contrast, the women, according to folk customs, went back to work on St. Distaff Day, the day after Epiphany. Today, January 7th. In an ideal world, St Distaff’s Day is the Sunday after Epiphany (January 11th), and Plough Monday is the next day. Of course, it doesn’t always work out that way. I am not sure the woman going back to work on the 7th January, would be happy with the men lounging about until Plough Monday? An extra 4 days off! Maybe, St Distaff Day was normally on the Sunday before Plough Monday?
Distaffs and Women’s Work
A distaff is ‘a stick or spindle on to which wool or flax is wound for spinning’. Because of its importance in the medieval and early modern economy, it became a synecdoche for women. St Distaff is a ‘canonisation’ of this use of the word. So, a day to celebrate working women.
We know that medieval and early modern women were a vital part of the workforce, despite the demands of childcare. Many women took on apprenticeships, even more continued their husband’s work after he died. Some professions like silk became a female speciality. Many taverns were run by the Alewife. Plus, London was full of female servants and nurses. Many women had several jobs.
The exhibition at the British Library on Medieval Women. In Their Own Words, indicated that most of the sex workers had two or more other jobs. But even if a woman remained solely in the domestic realm, the wife had to be mistress of a formidable range of technologies. Baking, Brewing, Cooking, Laundry, Gardening, Dairy, Medicine (including distillation), horticulture, spinning, sewing and embroidery. Even, aristocratic women did embroidery of the finest quality, and it often made an important financial contribution to the household. They also ran the household, which means they had to have a formidable range of managerial skills. Dealing with servants, managing the accounts etc.
Chatelaine.

The other symbol of ‘women’s work’ was the Chatelaine. The word also means keeper of the Castle. But women who controlled households had a clasp that hung from the waist. It was a bit like a Swiss Knife as it had the keys, and all sorts of other useful items. Here is an old photo of the Chatelaine from the collection of the Old Operating Theatre Museum, of which I was the Director for 25 years. From left to right it has a pencil, a little notepad, a pill dispenser, a pair of scissors, a little bucket that held a dose of medicine, a whistle to summon urgent assistance. These were not only useful but a symbol of authority for the Matron. 19th Century.
St Distaff Day and Plough Monday
Robert Herrick (1591–1674), born in Cheapside, London, a Goldsmith, priest, Royalist and Poet wrote in ‘Hesperides’.
Partly work and partly play
You must on St. Distaff’s Day:
From the plough, soon free your team;
Then come home and fother them;
If the maids a-spinning go,
Burn the flax and fire the tow.
Bring in pails of water then,
Let the maids bewash the men.
Give St. Distaff all the right;
Then bid Christmas sport good night,
And next morrow every one
To his own vocation.
Herrick, I think is suggesting fun and games are to be had. The men burning the flax and firing the tow, The women soaking the men with pails of water. In this piece, he links the plough team with St Distaff Day. This implies that the ploughs would be out on the next day. So as St Distaff’s Day is not always on a Sunday, perhaps Plough Monday is not always on a Monday? He certainly suggests everyone goes back to work either on St Distaff Day or on the day after,

Saints & Goddesses of the Distaff Side
In London, the Fraternity of St Anne and St Agnes met at the Church dedicated to the Saints. It is by a corner of the Roman Wall on the junction of Gresham Street and Noble Street. St Agnes is the patron saint of young girls, abused women and Girl Scouts. St Anne is the mother of the mother of the Son of God. So, together they represent the three generations of women: maidens, mothers, and grandmothers.
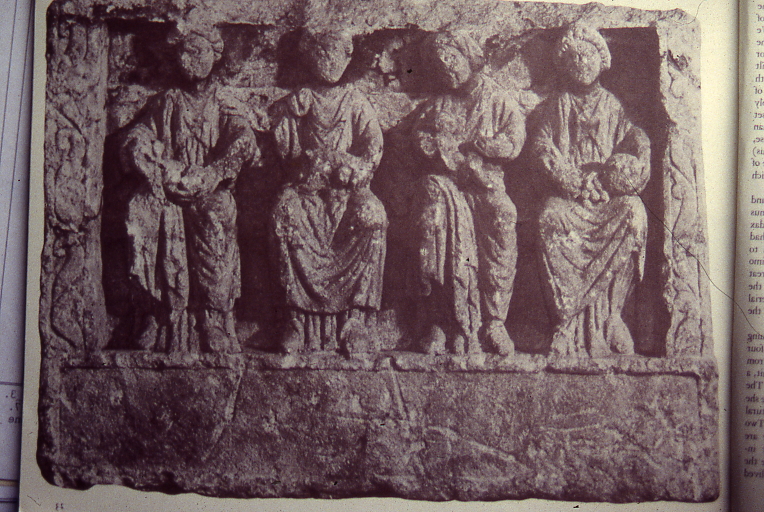

This trinity of women were worshipped by the Celts. Archaeologists discovered the sculpture above while investigating the Roman Wall a few hundred yards away at Blackfriars. Scholars believe it depicts the Celtic Three Mother Goddesses. The fourth person is a mystery, maybe the patron of a nearby temple? The relief sculpture was removed perhaps from a temple, or the temple was trashed at some point. Then the sculpture was used as rubble and became part of the defences of London.
The idea of triple goddesses is a common one. In Folklore and History they have been referred to as Maiden, Mother, and Crone, or even Maiden, Mother and Hag. They come in Roman, Greek, Celtic, Irish, and Germanic forms. Their names include the Norns, the Three Fates, the Weird Sisters, the Mórrígan and many more. The Three Fates, the Goddess Book of Days says, were celebrated during the Gamelia. This is the Greco/Roman January Festival to the marriage of Zeus and Juno. The Festival also gives its name to the Athenian month of January.
The Importance of the Grandma
The use of the terms Hag and Crone for the third Goddess is rare now, but was common. It does a great disservice to the importance of the Grandmother figure. (Although the original meaning of the words were less pejorative. For example, Hag may have meant diviner, soothsayer.) The three phases of womanhood are equally important to the continuation of the species. They provide love, support, and experience through the generations. Compare these three generations of supportive deities with Ouranos (Uranus), Cronus (Saturn) and Zeus (Jupiter). Saturn castrated and deposed his father, Uranus. Later, he tried to eat his son, Jupiter. But then, Jupiter is nobody’s idea of an ideal father. As one example, he eats his lover, Metis, to avoid her giving birth to his daughter, Athene. (See my post on the birth of Athena.)
Recent work on human evolution has suggested that the role of the Grandmother is crucial to our species’ ability to live beyond the age of fertility. Because, in evolutionary terms, once an individual cannot procreate, their usefulness for the survival of the genes is finished. So what’s the point of putting resources into grandma’s survival? The theory is the Grandmother has such an impact on the survival of the next generation, that longevity. for the female, beyond fertility makes evolutionary sense. Grandfathers less so.
Have a look at this site for more information.
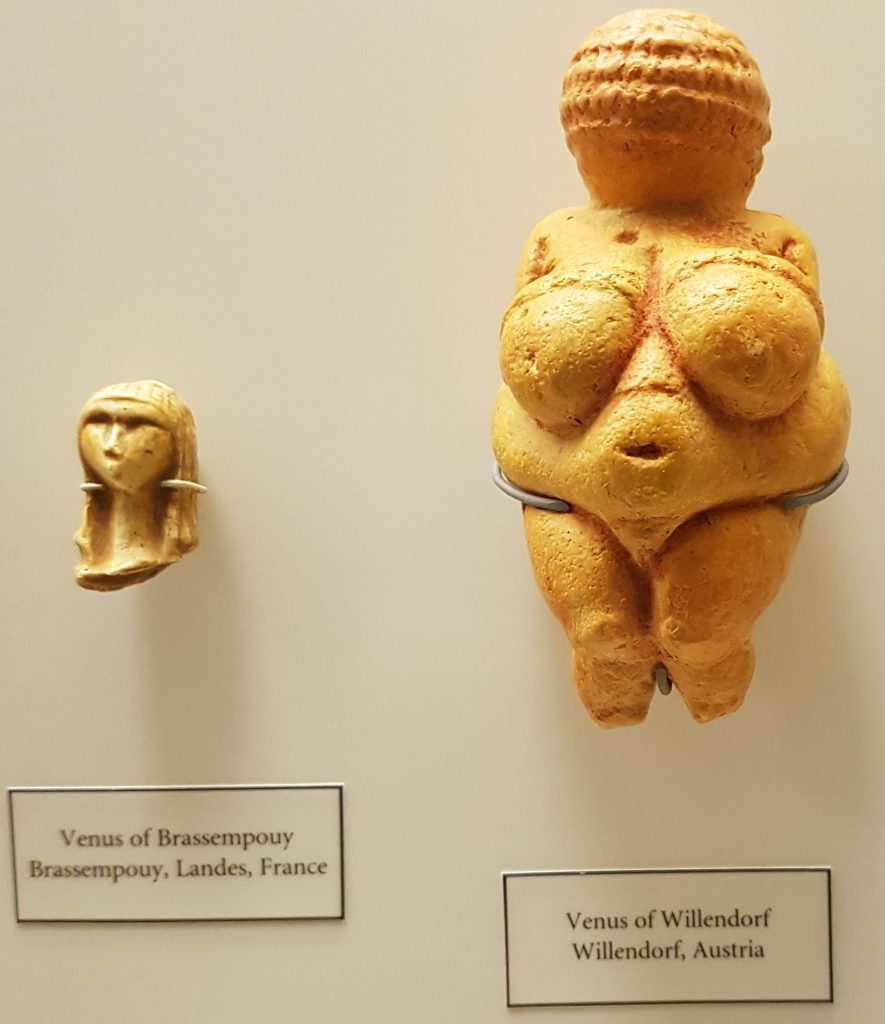

Venus of Willendorf
There was a theory widely held that the original Deities, dating before the spread of farming, were mother goddesses. The idea is that the hunter-gatherer goddesses (perhaps like the Venus of Willendorf) were overthrown by the coming of farmers. These patriarchal societies worshipped the male gods, which destroyed the ancient Matriarchy. Jane Ellen Harrison proposed an ancient matriarchal civilization. Robert Graves wrote some interesting, but no longer thought to be very scientific studies, on the idea. Neopaganism has taken these ideas forward.
More information on St Agnes look at my post on St Agnes and Keats.
One This Day
1451 Glasgow University was founded (and you wonder why the Scots made such an impact on the world.)
1789 The USA held its first national presidential election. (Long may that fine democratic tradition survive and prosper!)
1845. Today is the anniversary of the breaking of the fabulous Portland Vase by a drunken visitor to the British Museum. It looks immaculate despite being smashed into myriad pieces, a wonder of the conservator’s art. To see the vase and read its story, go to the BM web site here:

Today in the orthodox church, дед Мороз (Ded Moroz= father of frost), accompanied by Cнегурочка (Snieguroshka= fairy of the snow) brings gifts on New Year’s Eve, (which is on January 7th). He travels with a horse-drawn troika.
Today’s Interesting link
The pointy-shoed corruption of medieval London — for details, read the BBC’s interesting article.
First Published in 2022, and revised in January 2024, 2025, 2026