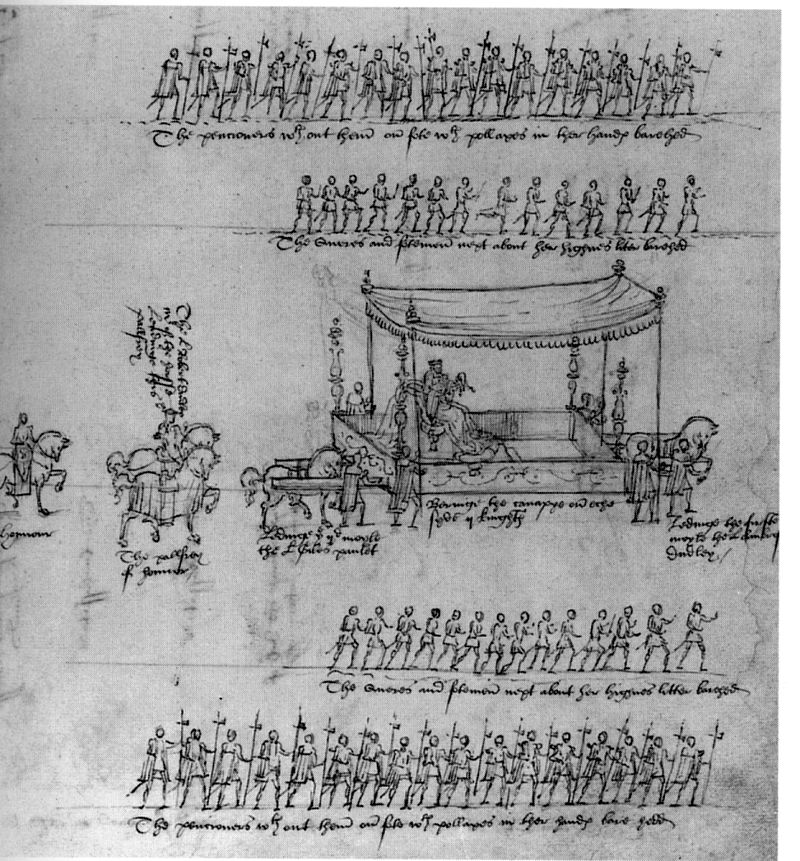
Today is the day after the anniversary of Queen Elizabeth 1’s coronation, 1559. She soon developed enduring relationships with the senior members of her Government. For example, William Cecil, Lord Burghley served the Queen for the rest of his life – from 1558 to 1598 when he died.
Queen Elizabeth I gave leading members of her Court, nicknames. I have been tracking them down. I eventually found a post in The Chronicles of History. The author is a follower of this blog. The Chronicles mentioned three of them, so I went in search for the rest, and here is what I found:
Her chief minister, William Cecil, Lord Burghley, was called her ‘spirit’ and her alleged lover, Robert Dudley, Earl of Leicester, was her ‘eyes’. Rather more cheekily, she called François, Duke of Anjou, her ‘frog’.
https://www.historyextra.com/period/elizabethan/7-things-you-probably-didnt-know-about-elizabeth-i/
List of Queen Elizabeth I’s Nicknames
Putting my various sources here is my ‘definitive list’.
Elizabeth called Robert Dudley, Earl of Leicester “Eyes”
William Cecil was “Spirit”
Robert Cecil was her “pigmy” or “elf”
Sir Christopher Hatton was “lids” or less flatteringly her “mutton”
Francis Walsingham was her “Moor”
Francis, Duke of Alencon, (her French suitor) her “frog”
http://everythingelizabethan.blogspot.com/2011/03/she-was-fond-of-nicknames.html
People on the list of Queen Elizabeth I’s Nicknames
A comment on the same page says the ‘moor’ was, in fact, Edward De Vere Earl of Oxford, suggesting the attribution to Walsingham is a mistake. De Vere had a house in Clapton, Hackney, very close to where I lived. De Vere is one of the strongest candidates (or so the conspiracy theorists say) to have written Shakespeare’s plays. Queen Elizabeth 1 has also been named a candidate for the world’s greatest playwright.
Robert Cecil was Lord Burghley’s son and largely took over his father’s role.
Christopher Hatton was a handsome aristocrat who had a lovely house and garden in Holborn. It is now a street called Hatton Garden, famous for jewellery and jewellery heists.
Francis Walsingham was the ruthless spy master that helped turn late Elizabethan England into a simulacrum of Stasi East Germany.
Duke of Alencon was one suitor she seemed to take seriously, although she gently mocked him.
Dudley was her favourite and almost her official escort/companion. (Did she have a sexual relationship with him?)
When I published this recently, I got an email from Jan-Marie Knights, an author, and she was able to persuade me that the Queen loved Dudley like a Brother, but never would marry him.
She showed me an extract from a book which has a letter saying the above – from Lord Burghley to his political agent in Germany. The book is The Private Character of Queen Elizabeth by Frederick Chamberlin (New York: Dodd Mead and Co, 1922).
Here is a photo of a page of the book with the letter.

Jan has published a book called The Tudor Socialite, which documents the ‘Tudor High life in bite-sized chunks.’
For a list of Gifts to Queen Elizabeth I have a look at the Folger Library page here.
For Queen Elizabeth I’s Coronation look at my post here.
On This Day
27BC Gaius Julius Caesar given the title of Augustus by the Roman Senate marking the official end of the Roman Republic.
Another example of how a system with elections and checks and balances can be subverted.
550AD Ostrogoths conquer Rome after bribing the guard.
1275 Edward I allows his mother Eleanor of Provence to expell Jews from Winchester, Cambridge, Marlborough and Gloucester
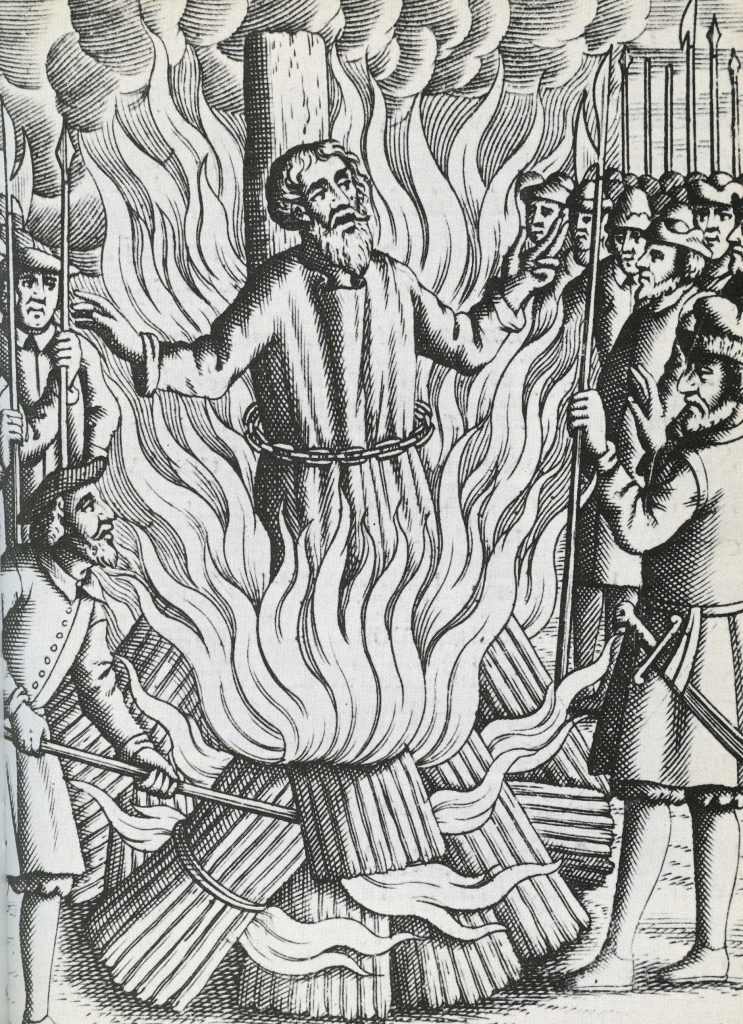
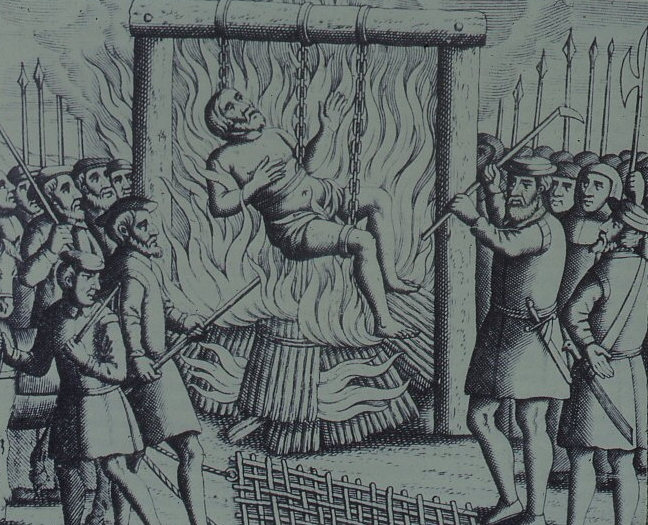
1537 Bigod’s Rebellion. Following successful negotiations between the Pilgrims of Grace led by Robert Aske, a new rebellion was led by Sir Francis Begod. It failed utterly buy leald to the rescinding of pardons. This saw Robert Aske hanged at York. Bigod and many others were also hanged. The female conspirator was dealt with as follows:
‘And the same day Margaret Cheney, ‘other wife to Bulmer called’, was drawn after them from the Tower of London into Smithfield, and there burned according to her judgment, God pardon her soul, being the Friday in Whitsun week; she was a very fair creature, and a beautiful.’
Wriothesley’s Chronicle
First Published in January 2023, republished in January 2024,2025, 2026