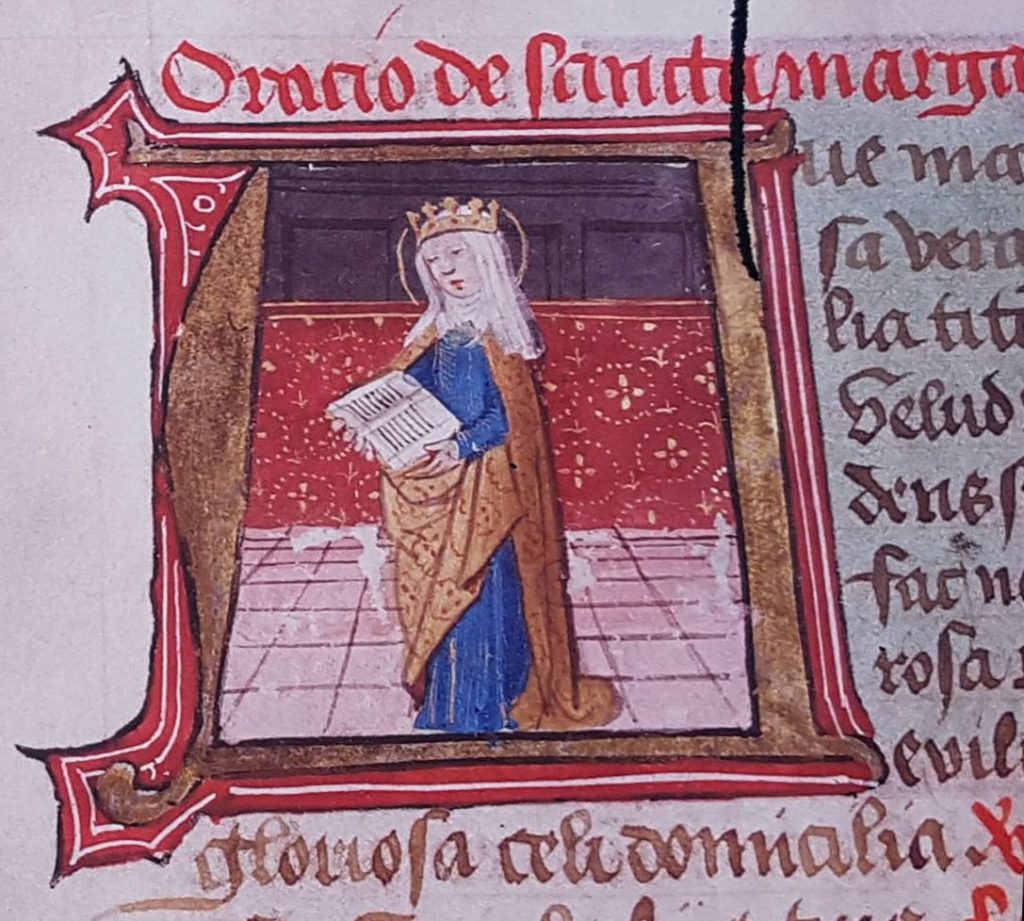
St Margaret should be better known in England because of her important rule in the bloodline of the English Monarchy. Her story is also of interest as it intertwines with the events of 1066 and of Macbeth.
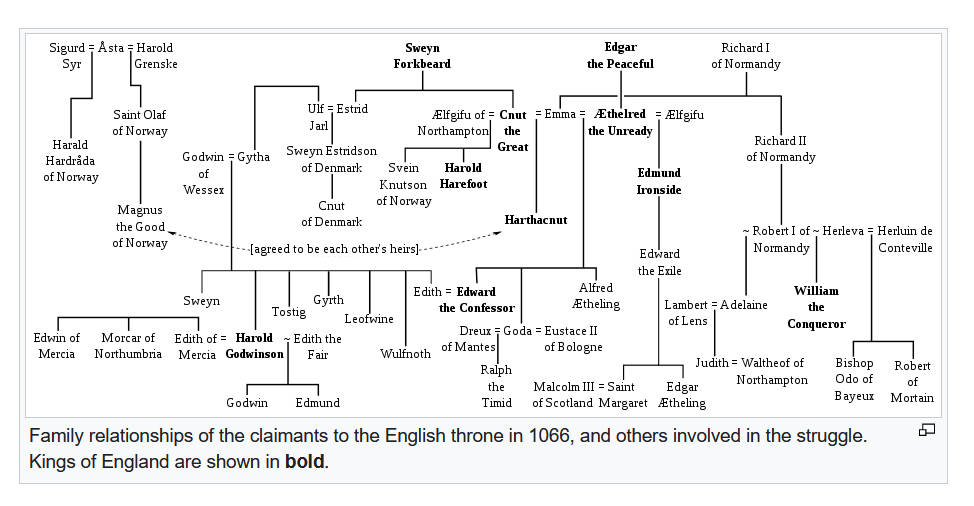
She was the granddaughter of King Edmund Ironside. He was the last English King before the Danish Kings took over. This is what a draft of the text for my book on the Kings of Britain says about him:
King Edmund II 1016
Edmund was born in around 988AD and nicknamed Ironside. He was a formidable warrior who spent his short life fighting the Danes. In 1016, he was crowned in St Pauls Cathedral. Although he was defeated in battle by King Canute, the son of King Swein of Denmark, Edmund’s prowess won him a peace treaty in which England was divided between the two Kings. Unfortunately, Edmund died unexpectedly and Canute inherited the Kingdom. Edmund was buried in Glastonbury Abbey.
To buy ‘Divorced, Beheaded, Died – the history of the Kings of Britain in Bite-size Chunks’. click here.
Edmund’s wife Edith and her 2 children were exiled to Sweden and then, somehow, got to Hungary. Edmund’s eldest son was called Edward the Exile and was married to Agatha. Margaret was their third child. In 1056 Edward the Confessor invited the family back to England and soon made Margaret’s father the heir to the throne. Unfortunately, he died in 1057. He was buried in St Paul’s Cathedral.
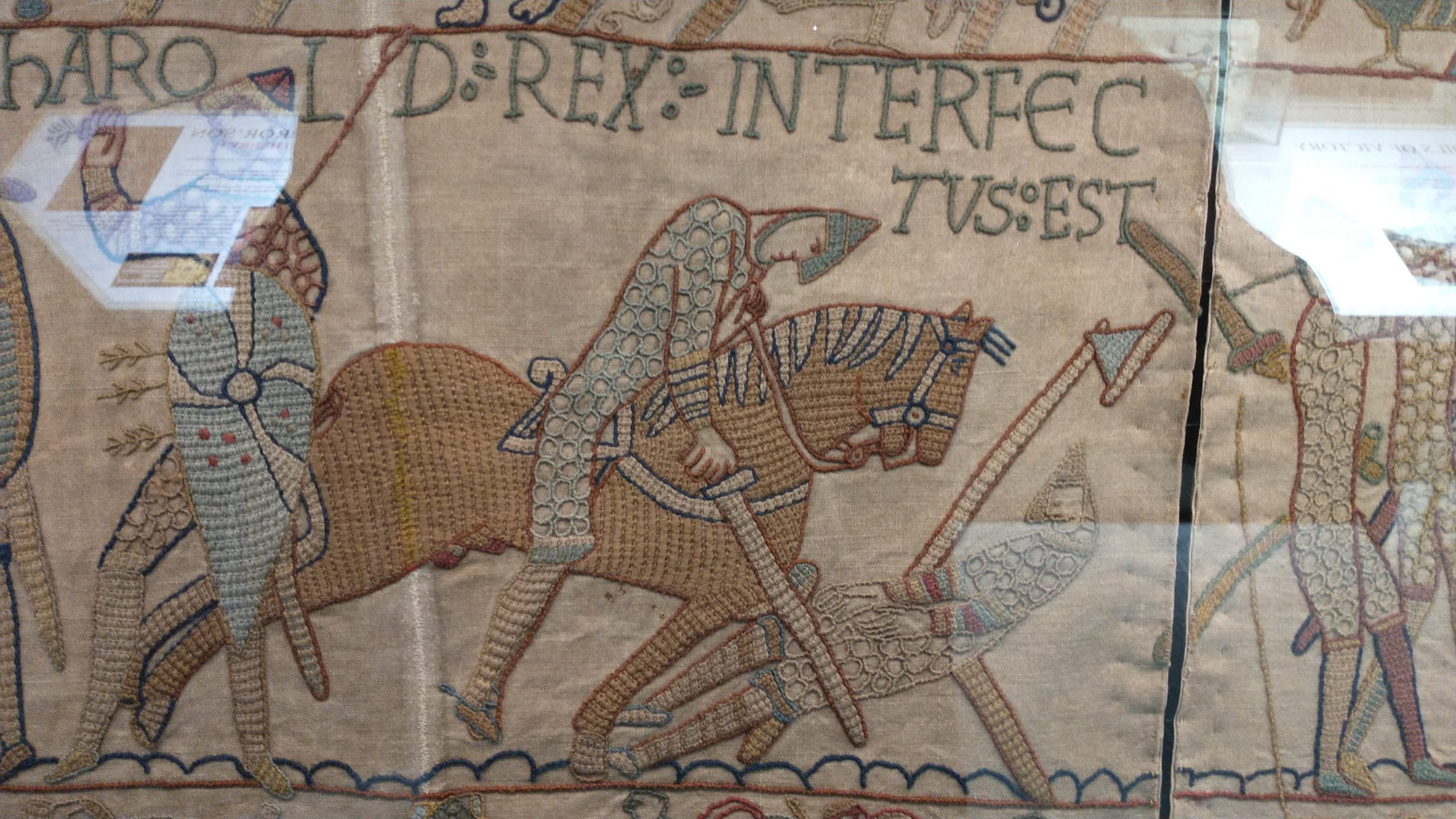
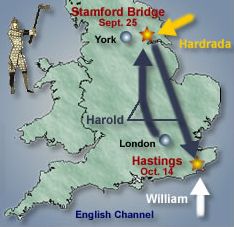
The rest, as they say, is history. Edward the Exile’s son, Edgar the Atheling was only 6 or 7 and the throne was disputed between William of Normandy, Harald Hadarada of Norway, and Harold Godwinson.
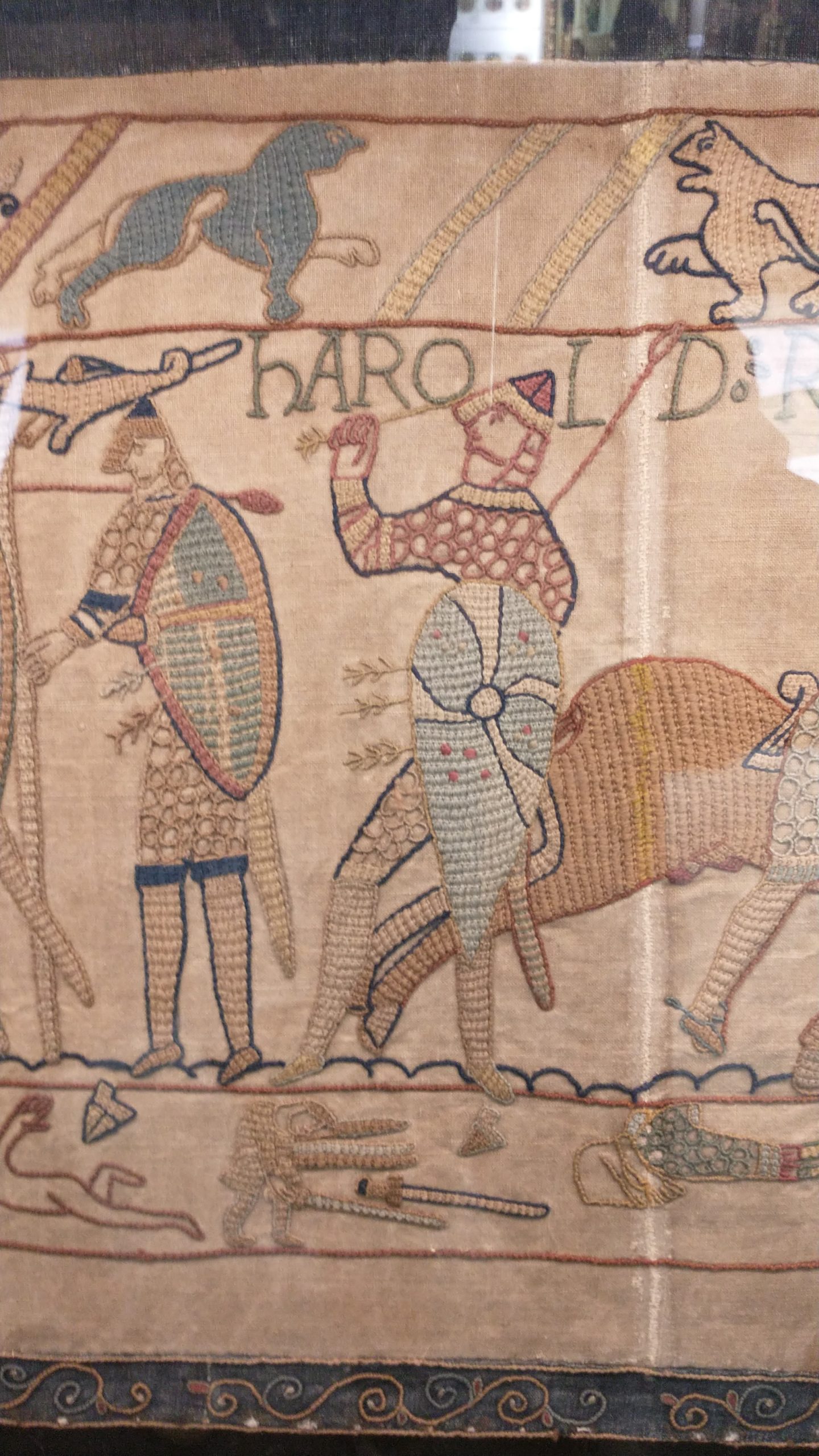
In short, Margaret’s brother Edgar the Atheling was briefly chosen as King after the death of Harold, but was forced to cede the throne to William the Conqueror, after the defeat of Harold Godwinson (Harold II). William was crowned King in December 1066. Margaret was forced to flee and went to Scotland.
You can read what happened, in my detail, in my posts on the three battles that decided England’s fate in 1066.
https://www.chr.org.uk/anddidthosefeet/battle-of-fulford-september-20th-1066/
https://www.chr.org.uk/anddidthosefeet/battle-of-stamford-bridge-september-25th-1066/
https://www.chr.org.uk/anddidthosefeet/william-the-bastard-invades-england-september-28th-1066/
https://www.chr.org.uk/anddidthosefeet/battle-of-hastings-october-14th-1066/
In 1070, Margaret married the Scottish King Malcolm III ( Mael Column Mac Donnchada).
Malcolm was the son of King Duncan (murdered by Macbeth – see my book Divorced, Beheaded, Died for a short biography). In 1040, Malcolm fled to England, but returned with English help to defeat Macbeth at Dunsinane. After his first wife’s death he married the deeply pious Margaret. Their court was very influenced by Saxon and Norman ways. She helped aligned the Church more closely with the rest of Christendom, and brought up her children piously.


The Royal couple had 6 sons and two daughters. Her son David became one of the most influential Kings of Scotland; introduced Norman ideas of feudalism, and created Boroughs to strengthen the Scottish economy. So, in many ways, Margaret had an influential role in ‘modernising’ the Scottish Monarchy from its Gaelic clan-based structure to a more European style that was ruled from the Lowlands and spoke the Scots version of English, rather than the Gaelic version of the Celtic branch of languages.
She died on 16th November 1093 AD and is ‘particularly noted’ for concern for orphans and poor people. There is an annual procession to her altar, followed by Evensong at Durham Cathedral on the following day. She was buried at Dunfermline following the violent death of her husband. The Abbey has recently celebrated the 950th anniversary of Queen Margaret consecrating the site.
Margaret’s daughter, Matilda, married the son of William the Conqueror, King Henry I. This marriage was important for the Normans because it added a strong dose of English Royal blood to the French Norman Royal line. Their daughter was the formidable Empress Matilda, designated heir to the throne of England and founder of the Plantagenet line of English Kings and mother of Henry II.
Matilda has a plausible claim to having been the first ruling Queen of England. But she was never crowned because of the disruption caused by the usurpation of the throne by King Stephen.
Margaret’s brother Edgar the Atheling had an extraordinary life, living into his 70s. He continued to fight against the Norman rule of England, mostly from Scotland. Eventually, he reconciled with the Norman dynasty but was involved in any number of disputes, rebellions and dynastic fights.
First Published on November 19th 2021. Revised on Nov 15th, 2023, and 2024