According to my Goddess Book of Days, December 11th is dedicated to Bruma the Roman Goddess of Winter. However, I’m not having much luck tracking her down. Elsewhere, I find reference to a Greek or Roman festival of Winter called Brumalia which, according to some, starts in late November and is normally said to end on the 25th December, the Roman Solstice. But, only the Goddess Book of Days has it on December 11th.

However, there is good evidence for such a festival in the Byzantine World.
So, let’s imagine a Winter Goddess beginning her reign on November 24th. Then, Saturnalia took place from 17th – 24th December and the climax of the reign of the Winter Goddess was Brumalia on the 25th December.
By the way, December 25th was fixed by Aurelian in 274 AD as the day to celebrate Sol Invictus, the Unconquered Sun, the pre-Christian Roman attempt to have a monotheistic element to their religion. Mithras and other Gods were also celebrated on December 25th.
Underlying this confusion of dates is the difficulty of aligning the solar year to the calendar year, and in the Roman period it was all over the place until Julius Caesar fixed the Calendar. (for more on that see my post here)
Roman Hoodie
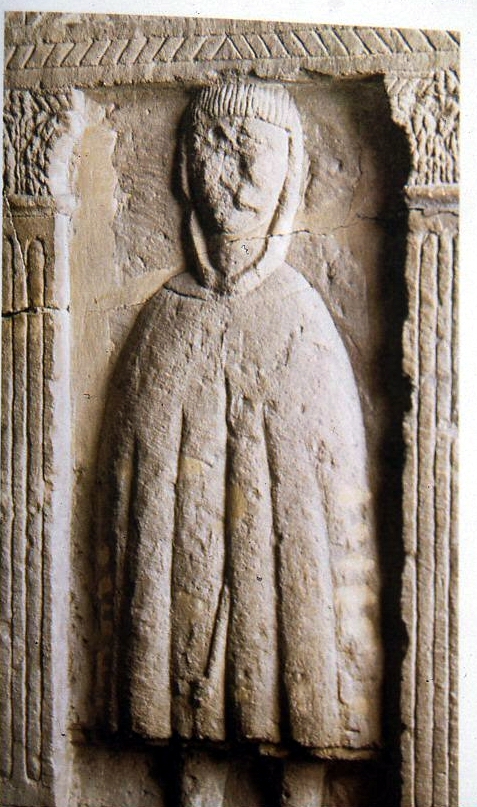
The picture of the tombstone, above, comes from Cirencester, and the inscription says:
Philus, son of Cassavus, a Sequanian, aged 45, lies buried here.
For details look at the ‘Roman Inscriptions of Britain.org’ here:
The Sequani were from the upper Saône Valley, near Besançon. His cloak is very interesting, and this type of hoodie has been found in other contexts of Roman Britain, for example, on a mosaic at Chedworth. The garment was called the Birrus Britannicus and was famous throughout the Empire. It was a hunting cloak and made of wool. The Cotswold wool was also famous in medieval Europe, and the Cotswold Lion sheep were introduced during the Roman period. The large number of rich Roman villas in the area suggest that the wool made the local economy strong, and. I imagine the birrus to be a sort of ‘thorn proof’ woollen garment that was warm, rugged, and waterproof. Britain was also renowned for the export of hunting dogs and slaves.
The British Hoodie, Inflation and Reorganisation of the Roman World
In AD 301, the emperor Diocletian issued his Edict of Maximum Prices. In it, the Emperor rages against inflation:
Greed raves and burns and sets no limit on itself. Without regard for the human
race, it rushes to increase and augment itself, not by years or months or else days, but almost by hours and very moments. Diocletian Maximum Prices Edict (click here for Pdf)
The Edict then lists maximum wages and prices. The birrus listing says that the Tailor,
‘cutting and finishing a hooded cloak (birrus) of the finest quality shall have a maximum wage of 60 denarii. ‘
The sanctions against breaking the Edict were terrifying, suggesting the difficulty of enforcement was compensated for by extreme punishment. Diocletian also insisted that labour shortages were addressed by making children follow the same profession as fathers. Interesting how familiar this rampaging inflation and severe staff shortages seems to a post-Covid-post-Brexit-Ukrainian-War-governed-by-an-out-of-touch-elite Britain. (Not quite so relevant now inflation is lower?).
Diocletian was obviously a very logical man, looking for structural fixes to society’s problems. His analysis of the Roman Empire and its frequent Civil Wars/Coup D’Etats/Usurpers was that there was a deficiency in the career ladder for megalomaniacs and so to stop them usurping the Emperorship, he set up a rational career progression and divided up the Empire as follows:
1 Augustus for the Eastern (Greek speaking) Empire
1 Augustus for the Western (Latin speaking) Empire
2 Caesars for each Augustus
Prefects reporting to the Caesars
Vicari reporting to the Prefects
Governors reporting to the Vicarius.
So you could begin your career in charge of a Province, then progress to the Diocese, then to the Prefecture, then to a quarter of the Empire, then to the Western Empire and finally to be the top dog in the richest Greek-speaking part of the Empire – the supreme Augustus.
Did it work? Well, while Diocletian was alive maybe, but then when his Augustus of the West Constantius Chlorus died, his troops, in York, declared his son Constantine to be Augustus, bypassing the peaceful progression from Governor to Augustus back to the usual tactic of wiping out your fellow Prefects, Caesars and Augustii. After the Battle of Milvian Bridge, Constantine was universally recognised as the supreme Augustus. He moved the Eastern Capital from Nicosia to Byzantium and renamed it Constantinople.

More on the Sequani
One of our readers from France alerted me to the Wikipedia page on the Sequani which explains that the name comes from the Goddess Sequana who is a water goddess. The centre of the territory is Besançon which is on the Doubs River part of the Haute Saône Doubs and near to the springs that are the source of the Seine (west of Dijon). Here, the Fontes Sequanae (“The Springs of Sequana”) gave her name to the River Seine, and a healing spring was established in the 2nd/1st BC. Enlarged by the Romans, it became a significant health centre. as Wikipedia explains in the clip below:

‘Many dedications were made to Sequana at her temple, including a large pot inscribed with her name and filled with bronze and silver models of parts of human bodies to be cured by her. Wooden and stone images of limbs, internal organs, heads, and complete bodies were offered to her in the hope of a cure, as well as numerous coins and items of jewellery. Respiratory illnesses and eye diseases were common. Pilgrims were frequently depicted as carrying offerings to the goddess, including money, fruit, or a favourite pet dog or bird.’
https://en.m.wikipedia.org/wiki/Sequana
First, published on December 11th,2022. Revised and republished on December 11th 2023, 2024