
Harold II was scurrying south after almost annihilating the Viking army of Harold Hardrada, when he heard news that the Normans had landed at Pevensey. (see my post (battle-of-stamford-bridge-september-25th-1066)
William was an unlikely Duke because it is very rare for illegitimate children to take the title of their father. It was normally not even considered as an option. A legitimate cousin or uncle would be chosen instead. But he not only got the title and survived many rebellions, but was known as the William the Bastard
He came to England in 1051 to see his distant cousin Edward the Confessor, who was the son of the English King Aethelred the Redeless (the ill advised – more often called ‘the Unready) and Emma of Normandy. Edward, whose marriage to Edith of Wessex was not great, insofar as both made claims to be holy virgins. So, Edward had no children. He, according to William, offered him the throne.
Did he, though? Well, the Pope agreed he did. William claimed that Harold of England accepted William as heir, too. And not only that, Harold, he said, agreed under Holy Oath.
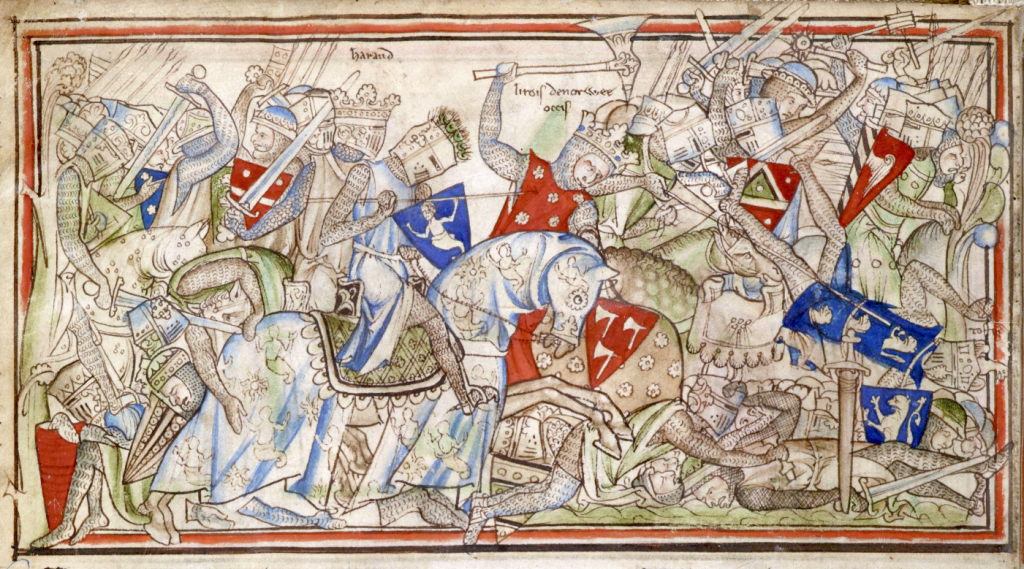
The Bayeaux Tapestry, shows Harold making an oath with his hands on holy relics. But British Historians believe it may never have happened. And if it did, then it was an inadmissable endorsement as it was not freely given, Harold had been detained on a visit in 1064. He was probably never going to get home unless he took the oath.
But the clincher for the English viewpoint is that Harold was the legitimate King because he was elected as was traditional by the Witanagemote, the King’s Council.
But was he really the legitimate claimaint? He had no English Royal blood in him, only a distant touch of Danish royalty on his mum’s side. It is true, that in England, the King’s Council or Witan elected Kings and often did not choose the first in line but preferred the best suited candidate be he brother, cousin or uncle. But Harold was only the brother of the King’s wife, no royal blood there.
However, Harold was so powerful that he would have prepared the ground for his election irrespective of whether this was the freely given choice of the Witan. His father, Earl Godwin, had been a disloyal and over mighty subject of King Edward, but had prepared the way for Harold to be virtual ruler of the country long before the King died.
So, even if the Witan’s endorsement clearly choose Harold there was plenty of scope for a contested succession.
In late September 1066 Harold was the English King who had already defeated the Norwegian claimant. Now, he was rushing to put to rest the Norman claim.
William Prepares for Conquest
William had begun by getting Pope Alexander II’s blessing for his claim to the English throne. He spent 10 months planning the invasion. He recruited adventurers from Normandy, France, Brittany, and Flanders. His allies collected boats for the invasion, while William had hundreds of new boats built, using thousands of carpenters, metalworkers, carters etc and cutting down a vast number of trees.
The boats were ready by 12 August near Caen on the River Dives. They set sail, but contrary winds blew them into Saint Valery-sur-Seine. Winds in the summer are usually blowing south on that coast, and William had a long, frustrating wait for a north wind.

Meanwhile, Harold was waiting with his army and a 400 ship navy at his manor of Bosham, near Chichester, on the South Coast. Then he heard about the Norwegian invasion of the North. He probably hoped it was getting too late in the year for William to risk invasion. So, Harold decided, on September 18th, to go North with his army, which was the more immediate risk to his throne.
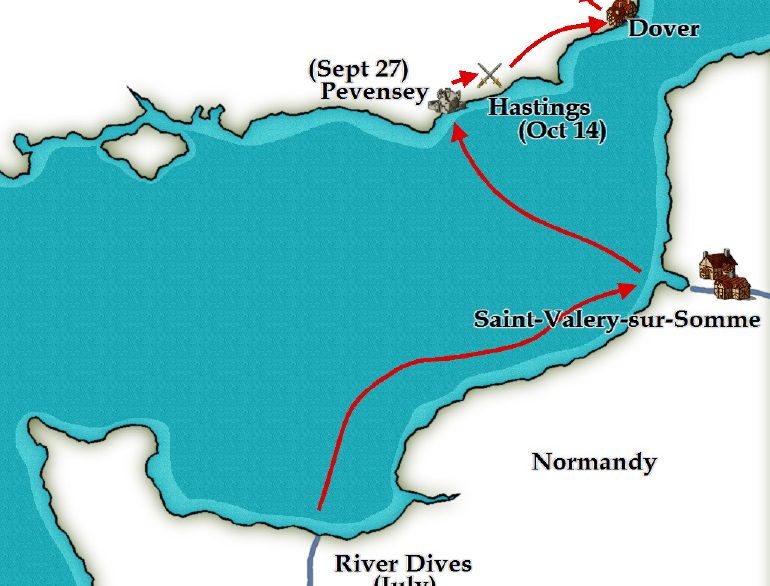
On September 27th, the north winds blew, the Normans embarked, and on the 28th of September William and his boat, given as a present to him by his wife, found themselves alone in the Channel off the English coast.
After an anxious wait, the rest of the fleet was spotted sailing towards William. They landed at Pevensey. Built a castle at Hastings and proceeded to ravage the land of Harold’s homeland. Harold had by now destroyed the Norwegian threat at Stamford Bridge on 25th September. He heard William had landed and rushed towards London
To be continued








![“To Concordia,¹ the Sixth Legion, Victorious, Loyal and Faithful and the Twentieth Legion [dedicates this].” found at Roman Corbridge (Coriosopitum)](https://www.chr.org.uk/anddidthosefeet/wp-content/uploads/2023/01/To-Concordia¹-the-Sixth-Legion-Victorious-Loyal-and-Faithful-and-the-Twentieth-Legion-dedicates-this..png)