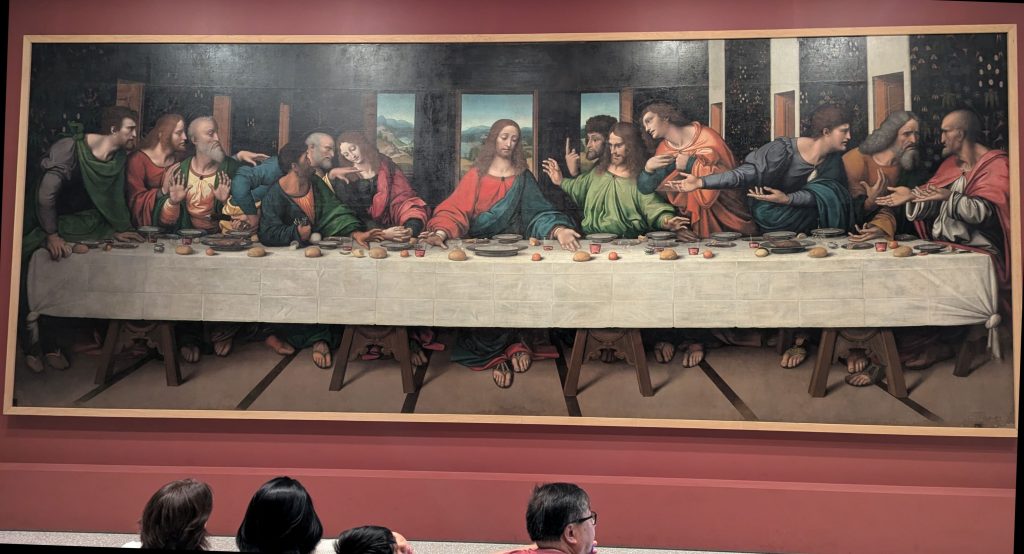
So, this is All Saints Day, Old style, also known as St Martin’s Day, one of the most important Christian festivals of the medieval world.
Father Francis Weiser in the Handbook of Christian Feasts and Customs suggests this was the Thanksgiving of Medieval Europe:
It was a holiday in Germany, France, Holland, England and in Central Europe. People first went to Mass and observed the rest of the day with games, dances, parades, and a festive dinner, the main feature of the meal being the traditional roast goose (Martin’s goose). With the goose dinner, they drank “Saint Martin’s wine,” which was the first lot of wine made from the grapes of the recent harvest. Martinmas was the festival commemorating filled barns and stocked larders.
It was celebrated with Bonfires in Germany, and with St Martins Beef and Mumming plays in England, but, following the Reformation, its place in the Calendar has been taken by Bonfire Day and Halloween.
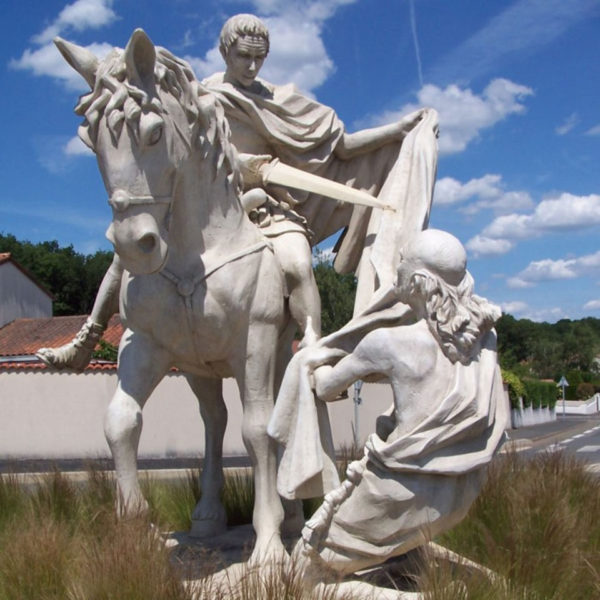
St. Martin of Tours (died AD397) was a soldier in the Roman Army who would not fight because of his Christian beliefs. When he met a beggar, he cut his cloak in half and shared his cloak. He rose in the hierarchy of the Gallic Church and became Bishop of Tours. He is one of the few early saints not to be martyred and is the saint of soldiers, beggars and the oppressed. Furthermore, he stands for holding beliefs steadfastly and helping those in need. According to legend, his barge on the River Loire was accompanied by flowers and birds.
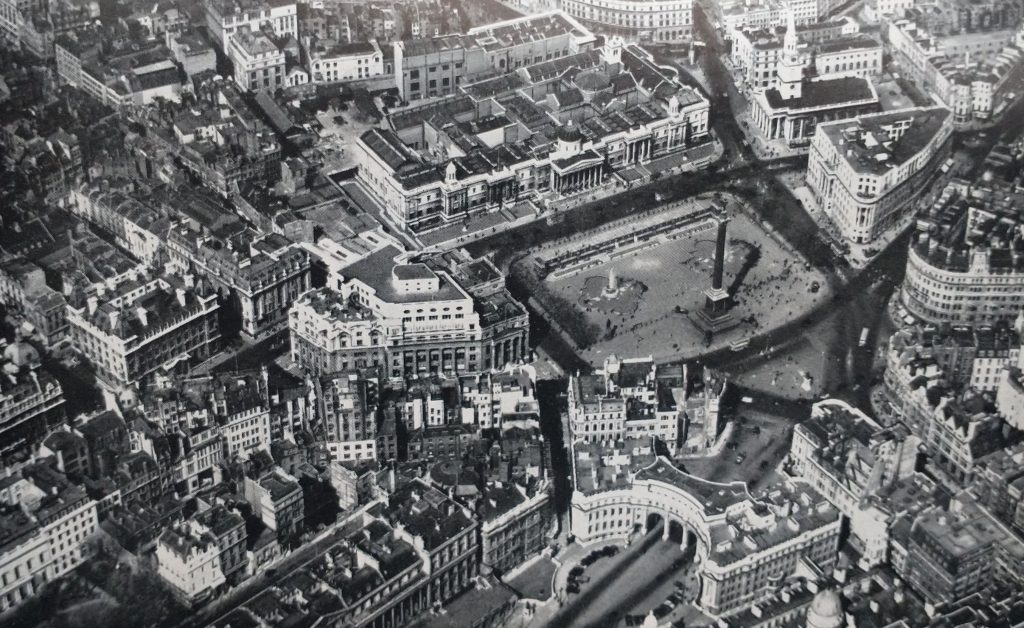

There are two famous Churches dedicated to St Martin in Central London with possible early origins. St Martin’s in the Fields, near Trafalgar Square, has been the site of excavations where finds show a very early settlement, with early sarcophagi. It is the one place where a convincing case can be made for continuity between the Roman and the Anglo-Saxon period. It is possible, that the Church was founded soon after St Martin’s death (397AD). A settlement grew up near it, and this expanded to become Lundenwic, the successor settlement to Londinium.
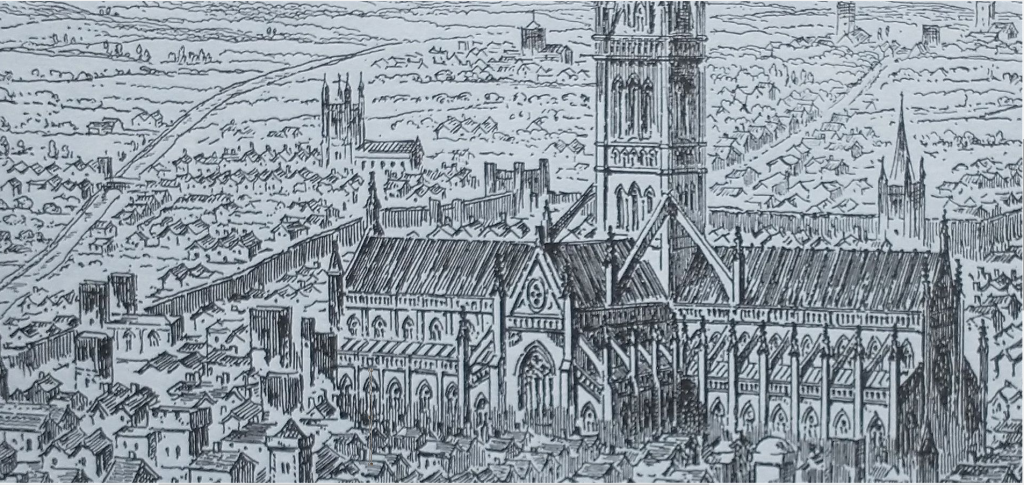

The other St Martins is St Martins Within, just inside the Roman Gate at Ludgate. Many early churches are found at or indeed above Gates and this one also has legendary links to burial places for King Lud, and for King Cadwallo, or Cadwallon ap Cadfan, one of the last British Kings to have any chance of recovering Britain from the Anglo-Saxons. Geoffrey of Monmouth says that Cadwallo was buried here in a statue of a Bronze Horseman, and thereby to protect London as a ‘Palladium’ (see for more about Palladiums of London. It has been suggested by John Clark, Emeritus Curator at the Museum of London, that Geoffrey of Monmouth might have used the discovery of a Roman Equestrian Statue as an inspiration for the story.
St Martin was also the saint of Travellers, and this might explain the location of the Church near the gate. Although there is nothing but legendary ‘evidence’, it would make sense for an early church to be built near Ludgate, which is the Gate that leads to St Pauls which was founded in 604AD. Although the City might have been mostly empty, the presence of St Pauls means that Ludgate was most likely still in use or at least restored around this period. It also leads, via Fleet Street and Whitehall, almost directly to the other St Martin.
St Martin’s Day was also the time of year when lime plaster was renewed because lime needs to be kept moist when renewed. It takes three to four days to form the calcite crystals that make it waterproof.
(Originally, posted 11 Nov 2021, revised 2022, 2023 and 2024)