We have various days to celebrate St Augustine of Canterbury. These are according to Google;
26 May (Anglican, Eastern Orthodox, and Catholic Extraordinary Form calendar in Great Britain)
27 May (Catholic Ordinary Form calendar)
28 May (Catholic Extraordinary Form calendar outside Great Britain).
Maybe like the Venerable Bede he died after Dusk! I give the explanation on yesterday’s post on the Venerable Bede.
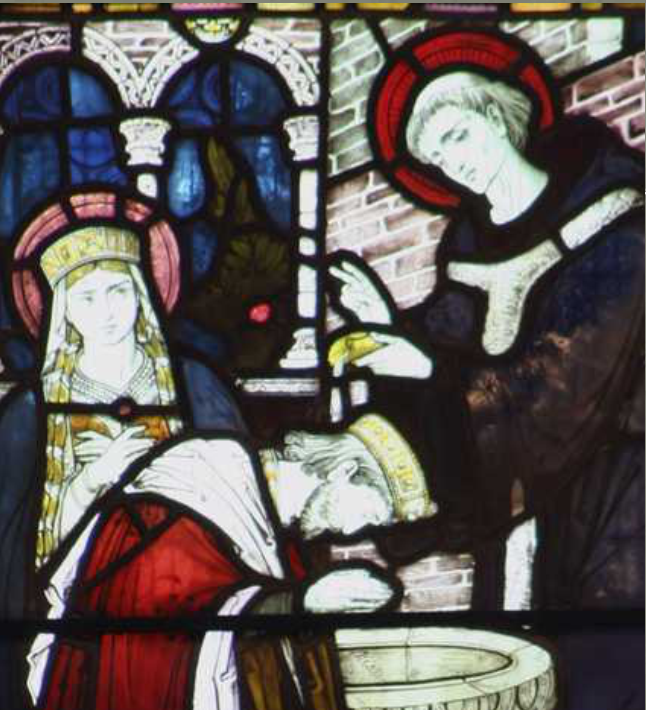
St Augustine brought Christianity to England, leading the mission sent by Pope Gregory to Canterbury in 597AD. He was the Abbot of a Monastery in Rome before the Pope sent him to convert the Angles. I tell the story of the mission in my post: March-12th-St-Gregory-Punster-Extraordinary/.
Augustine is the patron saint of England and the Anglican Communion. But he is not the person who brought Christianity to Britain. To England, maybe. Britain. No.
The Romans brought Christianity to Englands green and pleasant lands. I summarise the evidence in my post on St Lucius, who is claimed to have brought Christianity to Britain. Less controversially. Britain’s first martyr was St. Albans, who I will post about in June. However, some modern scholars doubt St Albans existence.
But there is good reason to think Christianity was strong in Roman Britain, particularly in towns. There is, also, some evidence of non-Christian religious centres surviving in the countryside. The Roman word for non-Christians, pagans comes from the Latin word paganus, which meant someone who lived in the country.
After the Romans, the Christian Church continued to thrive, with a host of Saints in Cornwall, and Wales. The first substantial eye-witness account of post-Roman Britain, dated to the early 5th Century, is by the Catholic Bishop Germanus. This shows a battle for souls in Britain not between Christians and Pagans, but between Catholics and other Christians. The Catholics targeted these as heretics. I talk about this in my post about St Germanus here.
The next insight comes from the conversion of the Irish to Christianity later in the 5th Century. St Patrick’s account gives an eyewitness view. What is interesting is that St Patrick’s family were living in a town where aspects of Roman life continued. After being kidnapped by Irish raiders, St Patrick went on to lead the conversion of the Irish. But he was helped by St Bridget and Palladius. See my post on St Patrick here, St Bridget here.
St Augustine & the British Church
I don’t think Augustine comes over with any sense of personality or charisma. But Welsh history shows him to be an unsympathetic, hierarchical character.
The relationship between the British Church and the incoming Roman Catholic hierarchy was strained. Meetings were held between the British Church and St Augustine. To prepare for this the British arranged a Synod in the old Roman town of Chester. Here 7 British Bishops and others prepared for their response to St Augustine’s insistence on the primacy of the Roman Catholic Church. One of the contentious issues was the ‘computus’ for deciding the date of Easter. Another was the style of the monks’ tonsure! But it was a major step for the British Churches to align themselves with a foreign ecclesiastical structure.
The delegates were advised by a wise hermit to arrive late at the planned meeting with St Augustine. Then they were to see how he reacted. If he got up and welcomed them, then he was a fit leader to follow. If he acted imperiously, he was not a man of God. St Augustine failed the test, the meeting was a failure. St Augustine cursed the British which is said to have lead to a military campaign against them by the Anglo-Saxons. The British lost the subsequent battle of Chester. It was said that 1200 monks from the nearby monastery of Bangor-in-Dee were slaughtered.
The battle severed the connections between the British Kingdoms in Cumbria and Scotland from the Kingdoms in Wales and made it very unlikely that the British would ever regain control of Britain from the English.
Bangor-on-Dee is a few miles from Chester and one of the most important British Monasteries. Among the clerics trained there are said to be Pelagius, who created the Pelagian Heresy which Germanus was sent to crush; Gildas the first ‘historian’ of the Saxon incursion. And St Tudno, who gave his name to Llandidno.
The two churches were finally reconciled at the Synod of Whitby. For more about the calculations for Easter and the Synod of Whitby look at my post here.
First written on 27/28th May 2025