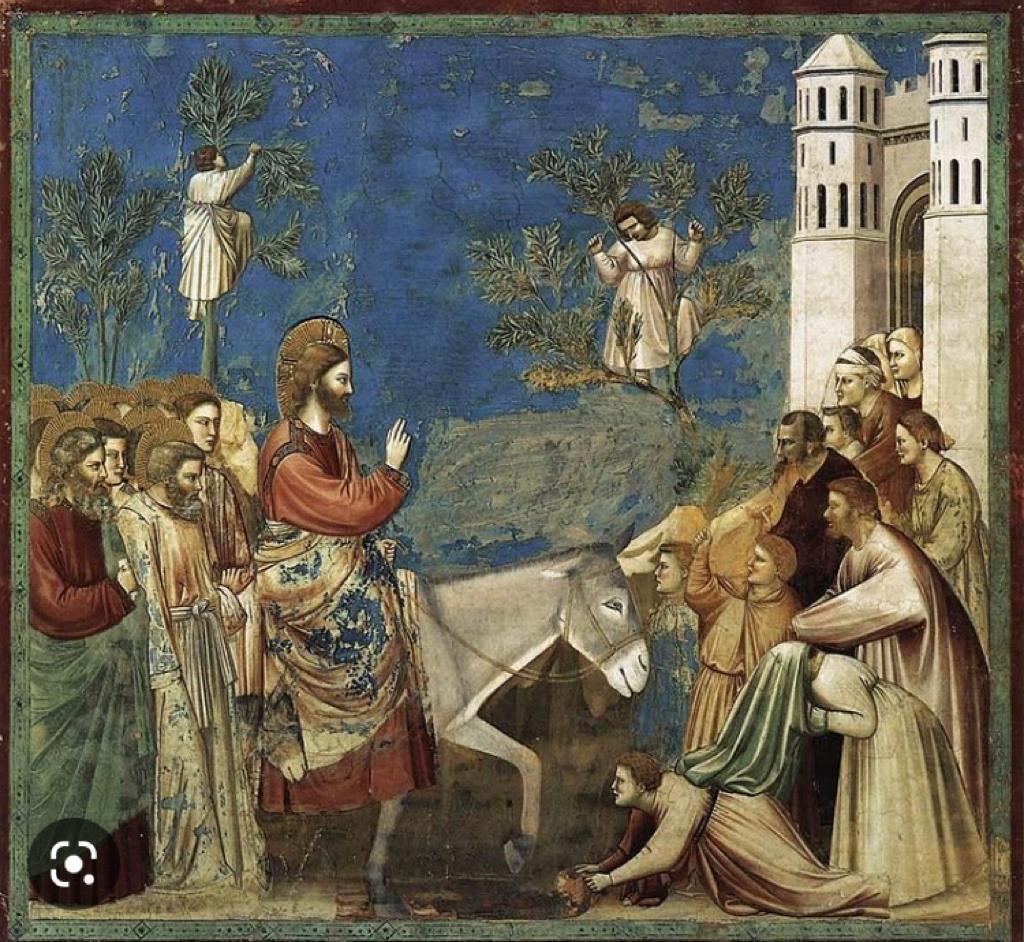
Monday’s child is fair of face,
Tuesday’s child is full of grace.
Wednesday’s child is full of woe,
Thursday’s child has far to go.
Friday’s child is loving and giving,
Saturday’s child works hard for a living.
And the child born on the Sabbath day Is bonny and blithe, good and gay.
Fortune-telling poems are a big part of folklore. It says something about the power of the rhyme that people can believe a random rhyme can shape someone’s whole life. Interesting that there are many versions of this rhyme. I chose one that had an optimistic Thursday. Two year’s ago, my second Grandson was born, on a Thursday, just like me. And I’ve still got far to go.
Tinker Tailor
The Tinker Tailor rhyme is another example of a fortune-telling rhyme. This is the extended version, I found on wikipedia.
When shall I marry? This year, next year, sometime, never.
What will my husband be? Tinker, tailor, soldier, sailor, rich-man, poor-man, beggar-man, thief.
What will I be? Lady, baby, gypsy, queen.
What shall I wear? Silk, satin, cotton, rags
How shall I get it? Given, borrowed, bought, stolen.
How shall I get to church? Coach, carriage, wheelbarrow, cart.
Where shall I live? Big house, little house, pig-sty, barn.
One person recites the power verse by verse. The subject of the fortune-telling does something like counting petals on a flower, counts bounces of a ball, or gives a number between one and four. The outcome determines the future.
To see another fortune-telling rhyme, read my post about Magpies.
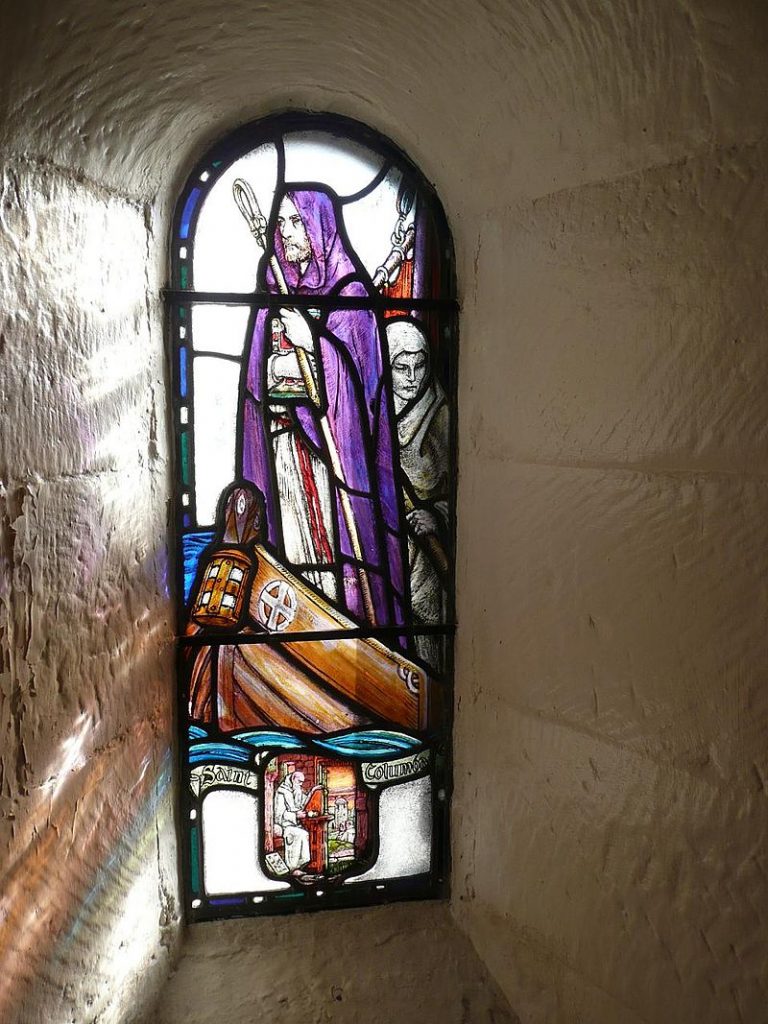
St Budoc
Today, is St Budoc’s Feast Day. However, it’s held on the 9th if you are in Brittany. Boduc is a Celtic name which either means “saved from the waters” or more likely ‘Victory’ or ‘Victorious’.
This etymology is shared by Queen Boudicca. Budoc lived in the 5th Century, after the Fall of Roman Britain. His mother was a Princess whose evil step-mother (or mother-in-law), persuaded her son that she was unfaithful. The Prince ordered the pregnant Princess to be thrown into the sea in a wooden cask. They floated around for 5 months, until Budoc was born. (Saved by the intercession of St Bride?). So, they landed safely in Cornwall, and afterwards went to Ireland. (Or they landed in Ireland.)
Eventually, Budoc’s dad realised his wife was faithful. So he came to rescue his wife. Sadly, they soon both died. (Or the wife survived). Budoc became a monk, and then a famous Bishop in late 5th Century Brittany at Doll. St Budoc is worshipped in several place: Pembroke, Cornwall, Devon, Brittany, and Oxford. But we have very little reliable evidence about him.
Monday’s Child published in 2023. St Budoc added in 2024, Revised 2025.