The Queen’s half share in the profits of the Golden Hind’s circumnavigation of the world, amounted to more than her normal annual income. So it is no wonder she knighted the Captain, Sir Francis Drake, in the dock in what is now South East London at Deptford. The Spanish were furious that a Pirate should be so honoured. The Queen may have given a French man the honour of dubbing Sir Francis. She did this, perhaps to encourage the French to support the English against the Spanish.
The annual Royal Income for King Charles III is £86.3 million. This is paid in the Sovereign’s Grant. It gives you an idea of Drake’s booty. But I imagine she had a greater share of the nation’s wealth than Charles, as she was the Government not just a honorific cutter of ribbons.
Francis Drake. Hero or Bloodthirsty Pirate?
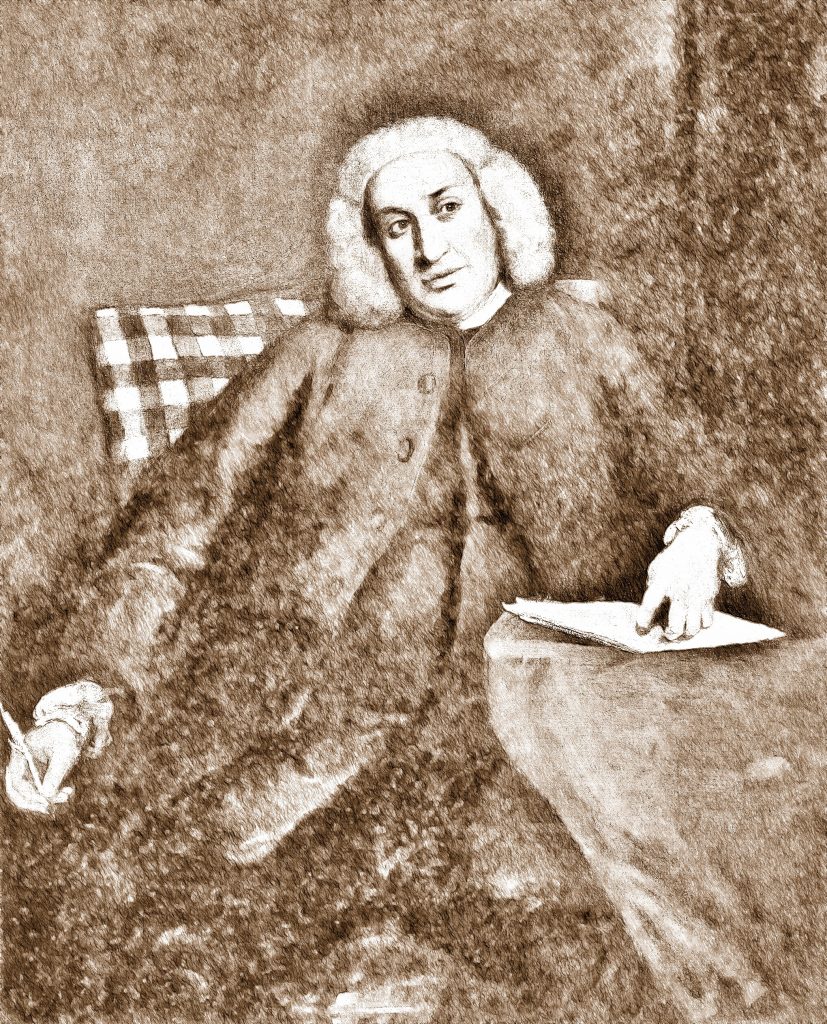
Francis Drake was one of the British heroes I read about as a child. I had a thick book with stories about people like Hereward the Wake, Drake, Charles II, Bonny Prince Charlie, David Livingstone etc. Many of them horrifically Imperialist and racist!
Drake was remembered for being the first English person to sail around the world. And his exploits in ‘singeing the beard of the King of Spain’ on his piratical raids on the Spanish Main.
In the books I read, the Spanish were the bad guys and we were on the side of the Angels. Drake was one of the swash-buckling heroes who turned Britain from a not very important country on the edge of Europe, to one of the World’s Great Powers.
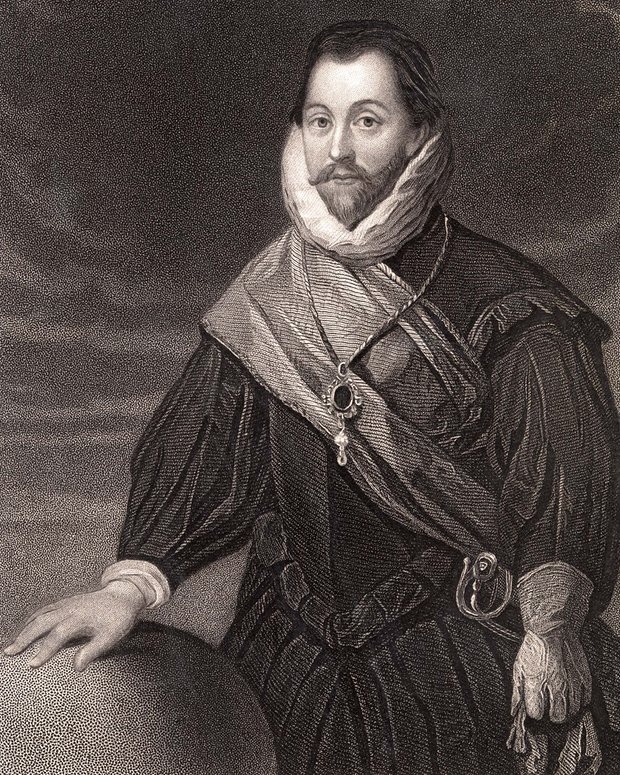

On the other hand, he was also a pioneer in the Slave Trade, was involved in atrocities in Ireland and in the Spanish Territories. He summarily executed one of his crew in dubious circumstances. Perhaps more significantly, his contemporaries did not entirely trust him.
Francis Drake and the Spanish Armada
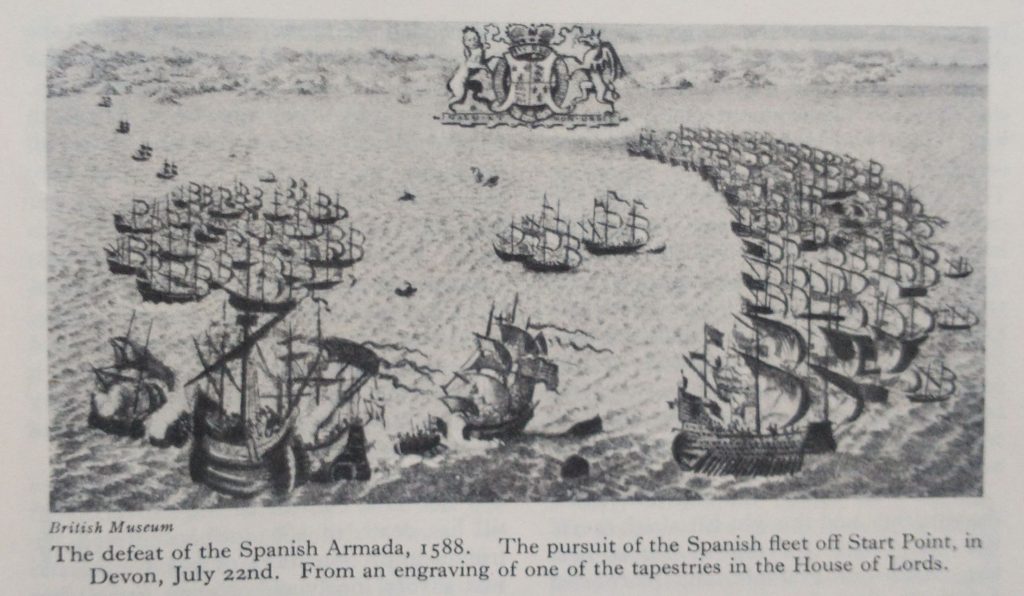
As the Spanish Armada sailed along the southern coast of England, the English Navy sniped at the heels of the Spanish. Drake was tasked with leading the night time pursuit of the Armada up the Channel. The idea was to stop them landing and to drive them away and into the North Sea. Drake in the Revenge was leading the pursuit, and the other ships were told to follow. He was to keep a single lantern alight in the stern of his ship. But the Lantern went out, and the British pursuit was disrupted.
The next morning, Drake comes back having captured the Spanish galleon Nuestra Señora del Rosario, flagship of Admiral Pedro de Valdés. The ship contained the gold to pay the Spanish Armada, which Drake seized. Was this a fortuitous accident which rebounded to Drake’s considerable financial advantage or something more deliberate?
In the end, the lantern incident did not stop the British forcing the Spanish to flee around the North of Scotland. On this perilous voyage only about 60 of their ships returned to Spain out of about 130. Britain was saved.
Nuestra Señora del Rosario and Agatha Christie
I used to lead an Agatha Christie program which included a visit to the Agatha Christie Poison Garden at Torre Abbey. And it was here that the captured Spanish ship’s crew were imprisoned after Francis Drake captured it.
The Abbey is now a lovely museum with the Poison Garden amidst the ruins of the Premonstratensian Abbey. Its tithe barn was used to hold the prisoners of war from the Ship. There were 397 of them. .
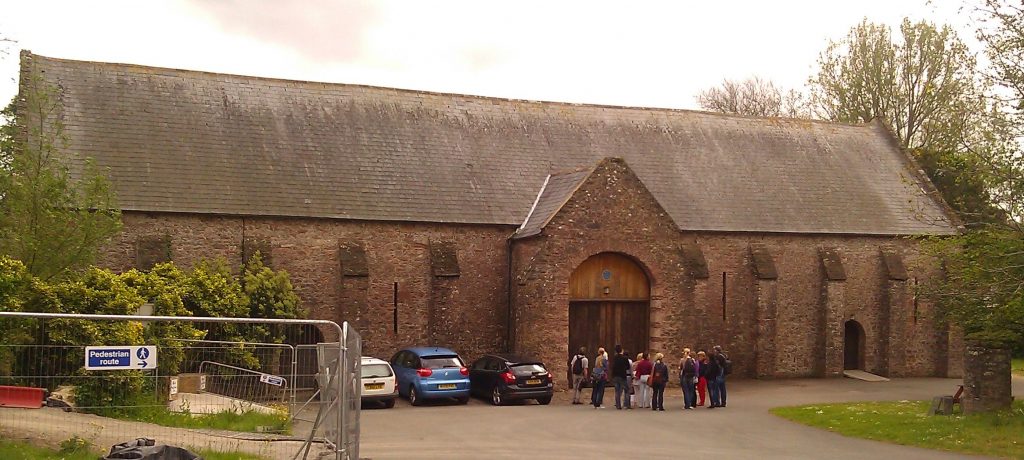

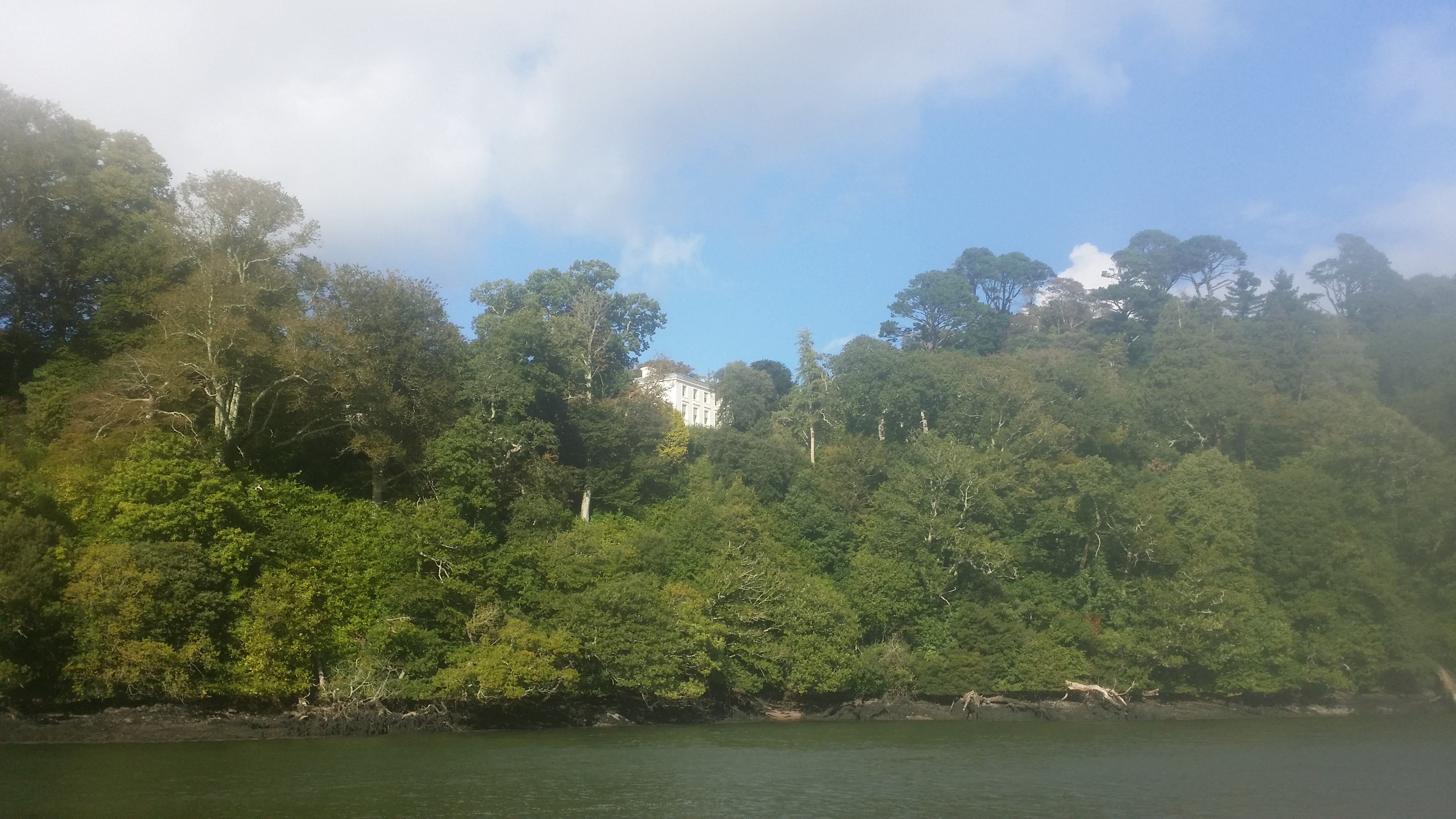
Sir John Gilbert, who was Sheriff of Devon at the time, used 160 Spanish Prisoners of War to develop his estate above the River Dart. The Estate is in a magnificent position, overlooking the drowned valley of the Dart. It is now enjoyed by those millions of visitors to what became the summer home of Agatha Christie (Greenway).


The Golden Hind & Deptford
Queen Elizabeth I decided that the Golden Hind should be permanently docked in Deptford. So the ship was placed in a ‘dry’ dock filled with soil. The ship decayed slowly with time, and by about 1660 nothing much was left.
I remember as a young archaeologist that some of our team took time out to work with Peter Marsden. He is one of the great experts in Naval archaeology, and he led a search to find Drake’s ship. There was a huge fanfare in the London newspapers. But, rather embarrassingly, given the build up, they failed to find anything of significance.
Another attempt was made in 2012. This also failed to discover any significant traces of an Elizabethan Galleon.

Golden Hind souvenirs
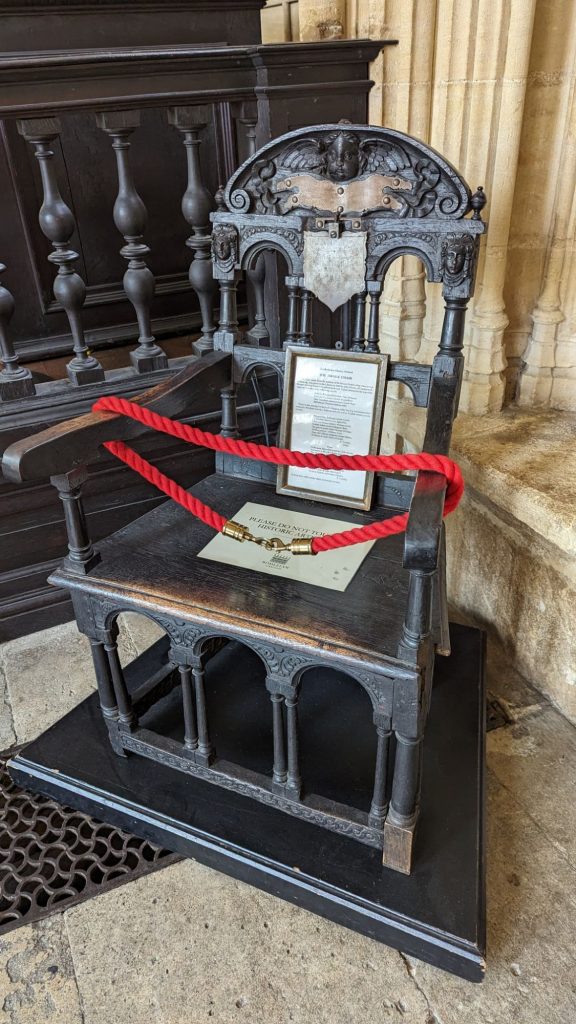
The Keeper of the Naval Stores at Deptford made chairs from the ruins of Drake’s ship, and one of them is on display at the Divinity Hall, Oxford.


Sir Francis Drake and Middle Temple Hall
In London, Sir Francis Drake was a regular visitor at Middle Temple Hall, off of Fleet St. A table (called the cupboard) is reputedly made from the hatch cover of the Golden Hind. This is where the newly qualified barristers stand to have their registration entered into the Inn’s books. Sadly, it did not survive the bombing of 1941.
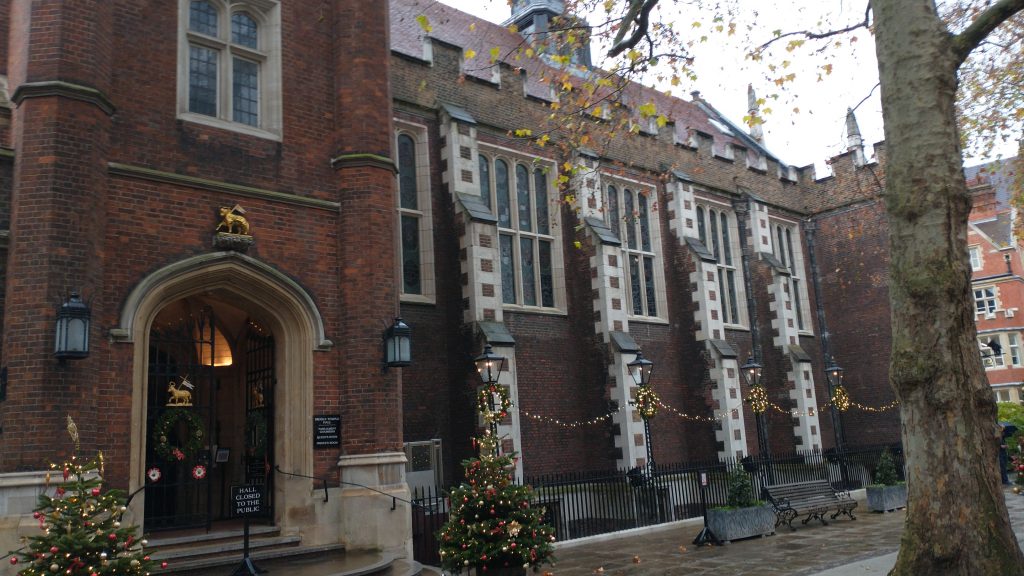

The lantern which hung in the entrance to Hall allegedly came from the ship’s poop deck (so not the one he failed to keep lit!). Other famous mariners are also associated with the Middle Temple including Sir Martin Frobisher and Sir Walter Raleigh. Shakespeare’s company performed Twelfth Night in the Middle Temple Hall
https://www.middletemple.org.uk/about-us/history/elizabethan-and-jacobean-times
Also on this day
The Romans celebrated the Great Mother, the Cybele in the festival of the Megalesia. To celebrate bringing of meteorite of Cybele to her temple in Rome in 204BC. Celebrated by the Games of the Great Mother
First published 2024, revised 2025