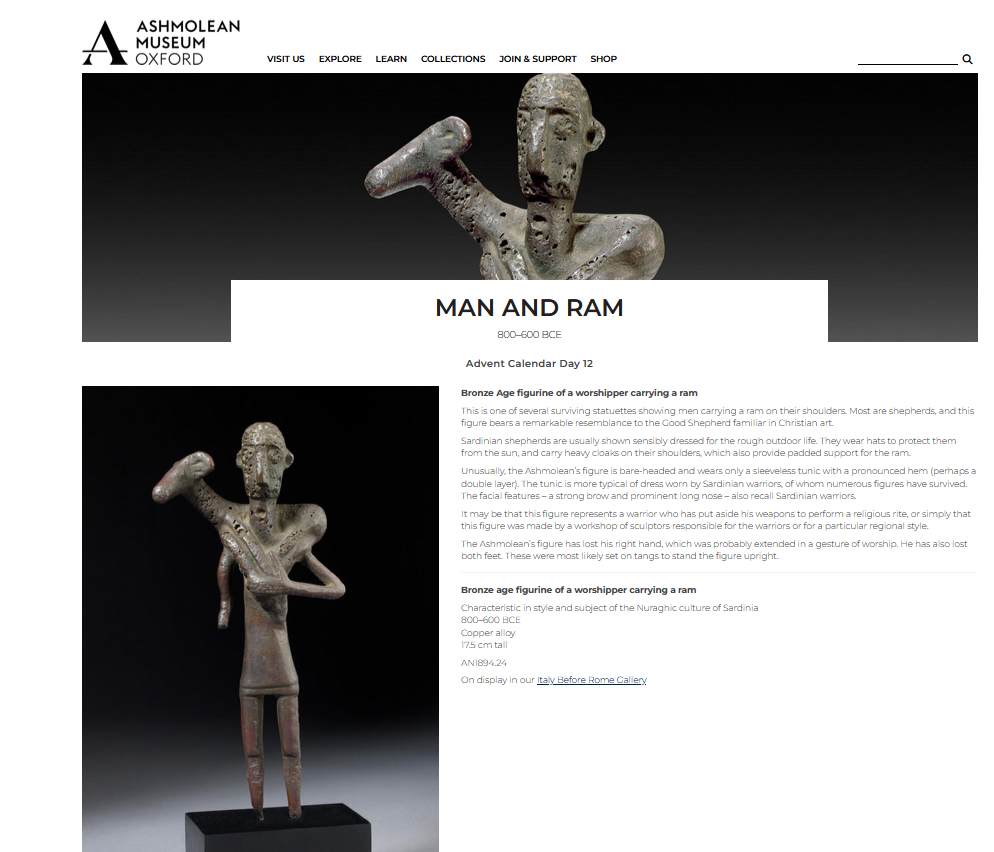
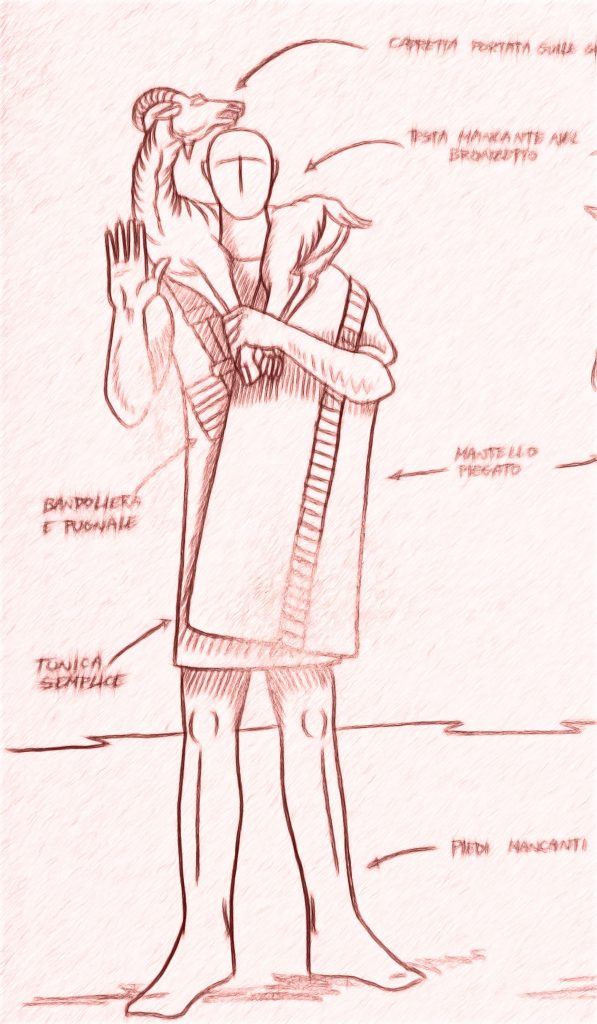
The First Day of Christmas, my true love sent to me a Partridge in a Pear Tree

Dies Natalis Solis Invicti
On the 25th December were born Jesus, Mithras, Attis, Saturn, Apollo, and the Invincible Sun.
The Sun Gods have quite a complicated interrelationship. Zeus, and Apollo are both also considered to be Sun Gods. Apollo is particularly interrelated to Helios, the Greek God who drives the Chariot that carries the Sun across the skies every day. The Romans had a God called Sol who some say was a deity who declined to be of minor importance, until the transexual Emperor Elagabalas and then Aurelian in 274 AD revived the cult. Sol Invictus was the focus of Constantine the Great, and has been suggested as a response of the Romans to a trend towards monotheism in the later Roman period. Sol for Constantine was a gateway God to Christianity.
It is also notable that early worship of Jesus is full of solar metaphors, Jesus being, for example, the light of the world. Churches are also virtually all orientated East West, aligned with the rising and setting suns. The Altar is always at the East End, and effigies on tombs face the East.
Did the Celts have a sun-god? Belenos is a contender, but linguists are proposing his name does not come from words meaning bright but from strong. The God Lugh’s name is suggested to mean ‘shining’ but his attributes are more of a warrior than a sun god. Taranis is probably the best candidate, but he is more of a sky or thunder god than specifically a sun god. However, his symbol is a wheel and the wheel is symbolic of the turning of the year.

The Golden Wheel from Haute Marne in France, (Public Domain, Wikipedia)
His 8 spoked wheel is said to be symbolic of the Sun and it represents the division of the year by the 4 quarterly sun festivals (Winter Solstice, Spring Equinox, Summer Solstice and Autumn Equinox) and the 4 cross-quarter festivals, (Samhain or Halloween, Imbolc or Candlemas, Beltane or May Day, Lughnasa or Harvest Festival).
December 25th is a few days after our reckoning of the Solstice but it was the date of the Roman Solstice.
Christmas Cake
Today, you might be tucking into a Christmas Cake (originally eaten on Twelfth Night). Now, I know many Americans have a bizarre belief that fruit cake is the cake of the devil, something you receive as a gift and give away to someone else, as most Americans hate it. More fool them for missing out on one of the delights of the Christmas period, that and cold turkey sandwiches. Christmas Cake is made on stir up Sunday, the last Sunday in November, to let the ingredients develop their flavour. They are then covered with marzipan and decorative icing.

In Germany, they also eat a fruit bread called Stollen or Weihnachtsstollen. The tradition is said to have been started in the 15th Century, when the Pope gave dispensation to allow the use of butter in the fasting period of Advent. The Germans had to use oil to replace the banned butter, but they could only make oil from turnips, so eventually the Pope allowed the use of butter, with which they made bread with added dried fruits.

In Italy, they eat Panettone, a fruit bread/cake. It is a sourdough, and a cross between a brioche and a cake. It often comes in a beautiful decorative tin, and is delicious. The centre of panettone production is Milan and this year is the 200th Anniversary of Milan’s famous Marchesi 1824 which makes artisanal Panettone from ‘fine ingredients such as six-crown sultanas, naturally candied fruit, Bourbon vanilla from Madagascar, Italian honey and eggs from free-range hens, blended in a slow-rising dough with the exclusive use of Marchesi 1824 sourdough starter‘. Thank you, Mara from Milan, for the heads-up.
Which is best? The only way to find out is to eat several slices of each. America, you don’t know what you are missing.
For stir up sunday see the second half of this post of mine.
First Published 24th December 2022, Republished 25th December 2023, 2024