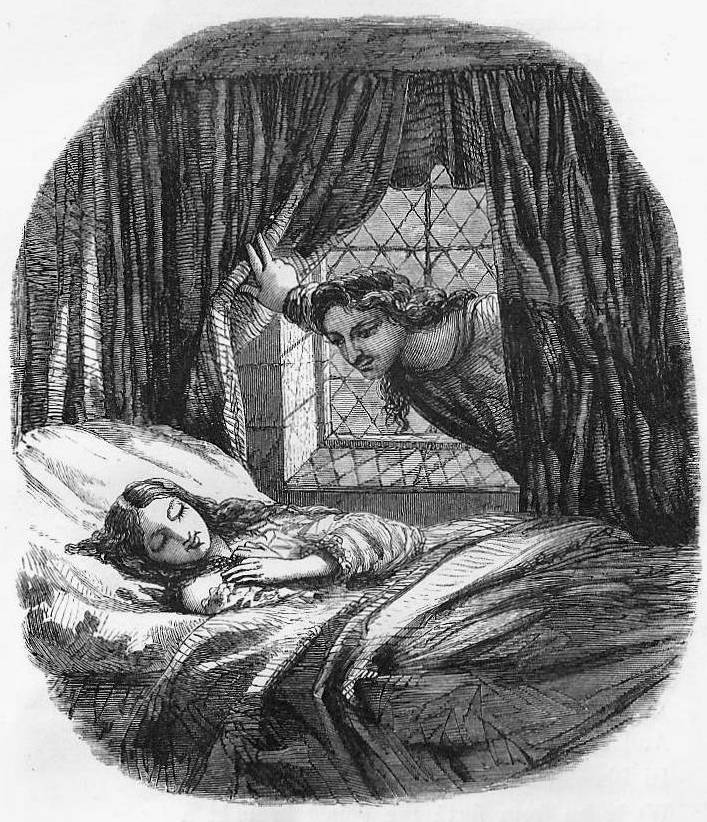
St Valentine’s Day in a Poem by Chaucer
| For this was on Seynt Valentynes day, | |
| Whan every foul cometh ther to chese his make, | |
| Of every kinde, that men thynke may; | |
| And that so huge a noyse gan they make, | |
| That erthe and see, and tree, and every lake | |
| So ful was, that unnethe was ther space | |
| For me to stonde, so ful was al the place. |
This is my ‘translation’
For this was St. Valentine’s Day
When every bird came there to chose their mate.
Of every type, that men think may
And that so huge a noise did they make
That earth and sea and tree and every lake
So full was, that hardly was there space
For to stand so full was the place.
St Valentine’s Patronage
This is the first reference to St Valentine’s as a romantic day. And some people charge Chaucer with making the whole thing up! St Valentine, is supposed to have been martyred in the 3rd Century (290AD) on the Via Flaminia on February 14. He refused to stop marrying people in the Christian rites. Therefore, he is the patron Saint of lovers. Valentine is also the patron Saint of epileptics, fainting and beekeepers. According to legend, he taught a young blind girl how to look after Bees, and, sometime later, her eyesight was restored. He also is said to have treated a young man of epilepsy. Epilepsy was sometimes called the Falling Sickness, and so he is also the Saint of Fainting.
But until Chaucer, there was no particular link with romance. In fact, there are at least three Saint Valentines who were martyred in the Roman period. Their relics are scattered around Europe (have a look at this National Geographic article for the full S.P.). These include bones in Glasgow and his heart in Dublin. There are in total 11 Saints called Valentine in the list of Catholic Saints.
Another theory is that St Valentine has taken over the aspect of the God Cupid, as a Christian attempt to create a holy festival to replace the Lupercalia. See my post on the Lupercalia here.
St Valentine’s Day and Birds
Chaucer’s poem suggests one possible route to the link with romance. Early February is about the time when birds pair off. If they want to have their chicks at the optimal time, then they need to get going before spring has really sprung.
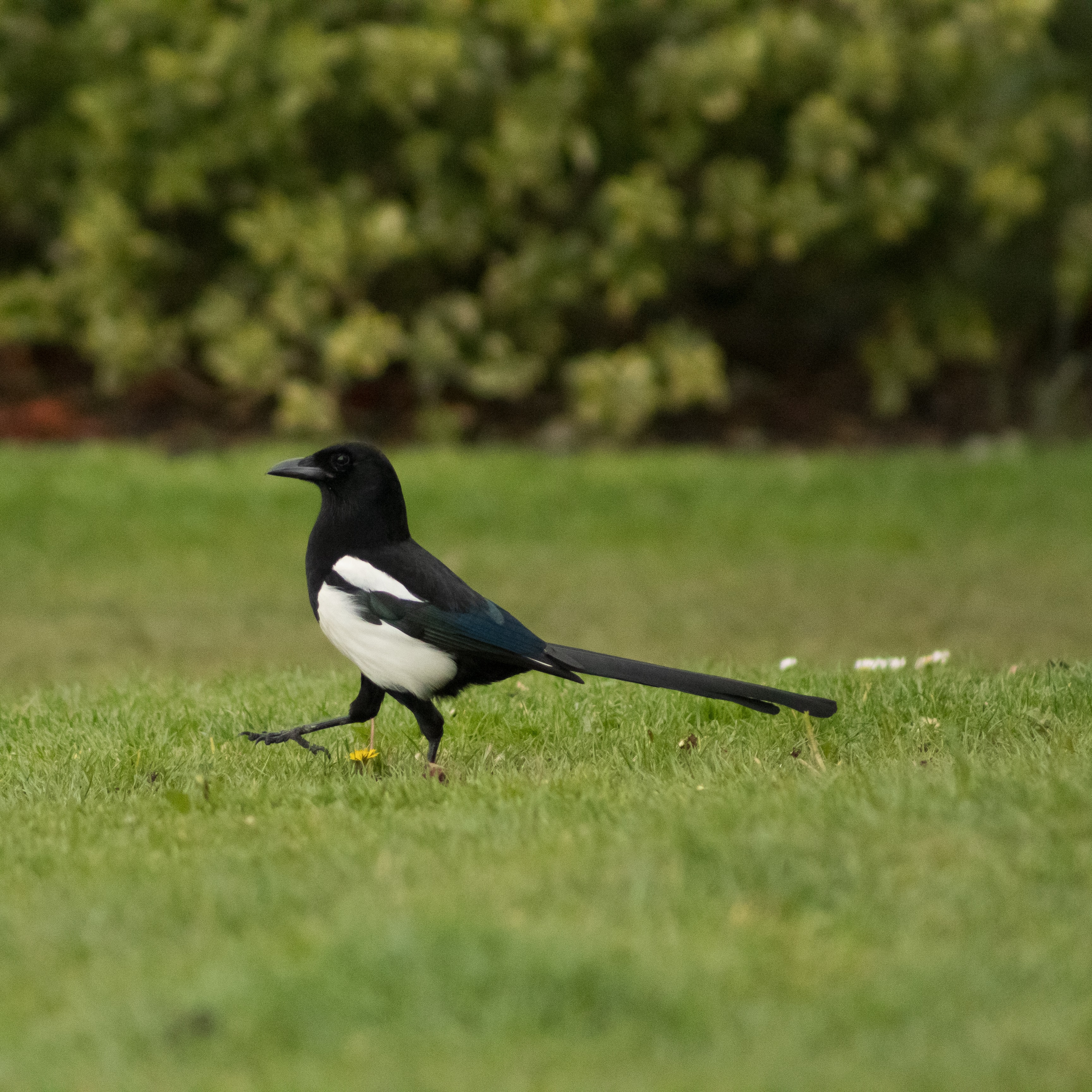
When I think of love, I don’t think of birds. Maybe, this is because I live by a Canal. Outside my garden, I frequently see and hear a Coot chasing his pair across the water before violently mounting her. But then they are fiercely monogamous and defend their nest, fearlessly, against much bigger birds. And swans glide by in beautiful family groups. But Magpies are my favourite lovebird because you see one, and then look around, and you very often see the partner. I have adopted an old tradition that you are supposed to say:
‘Hello, Mr Magpie! Where’s Mrs Magpie?’
And look for the mate. It is good luck if you see her and bad luck if you don’t. (Please feel free to assign your own favourite gender!)
‘One for Sorrow’ is a well-known nursery rhyme found in many variations, and is an example of ‘ornithomancy superstition’ whereby the number of Magpies you see determines some aspect of your future. Magpies normally mate for life, and are not gregarious during the nesting season, but thereafter, they ‘join together in large wintering flocks of more than 20 or so birds.‘. So, perhaps we need at least another seven lines for the rhyme? So, far I have never seen a flock of them. If you have a photo of a flock, please send it to me!
One for sorrow,
Two for joy,
Three for a girl,
Four for a boy,
Five for silver,
Six for gold,
Seven for a secret,
Never to be told.
Eight for a wish,
Nine for a kiss,
Ten a surprise you should be careful not to miss,
Eleven for health,
Twelve for wealth,
Thirteen beware it’s the devil himself.
As to the likelihood of seeing thirteen magpies together – well I have seen them often in pairs, occasionally in threes and often alone.
Here is another, more dangerous version of the rhyme (you are more likely to see the Devil)
One for sorrow,
Two for mirth
Three for a funeral,
Four for birth
Five for heaven
Six for hell
Seven for the devil, his own self
For details of the history of versions of this poem, click here:
Bad Birds
Magpies don’t have a good reputation, traditionally being regarded as thieves and scavengers with untidy nests and eating habits. They are supposed to be attracted to shiny things, but Exeter University did some research which found that they have the normal Corvid’s curiosity for objects. But they are as happy to snatch a dull object as a shiny one. So, we can see they are very intelligent as well as faithful lovers. For me, a good-omened bird (as long as I see the two of them).
More on Chaucer in my post for April 18th. For my post on Blackbirds see here.
On This Day
44BC – Julius Caesar was appointed dictator in perpetuum. Or perpetual dictator of the Roman Republic. Coins were issued with the phrase DICT PERPETVO.
1400 -Richard II died shortly after Epiphany Rising, a failed plot to restore him to the throne. Some think he was starved to death in captivity in Pontefract Castle. Or he starved himself. His body was taken to London and put on display in St Paul’s Cathedral on 17 February. His remains were taken to one of his favourite palaces at King’s Langley Priory on 6 March. Henry V had his remains ‘translated’ to Westminster Abbey. King’s Langley was a Royal Palace lived in by Eleanor of Aquitaine and Edward II, as well as Richard II. It is near Slough.
Jan-Marie Knights author of The Plantagenet Socialite lists possible scenarios:
‘The accepted tale of the king’s death is that in despair and grief at the death of his friends, King Richard refused to eat or drink, although a few say he was purposely starved to ensure he died as if from a natural death. Another rumour is that when an esquire mentioned the words ‘King Henry’ while he was eating dinner, Richard struck him with the knife he was using. Guards charged in and the king, pushing the table away, took a bill out of one man’s hand and managed to slay four of them but one leapt onto the chair he had vacated and felled him with a stroke of his poleaxe.’
1876 – Alexander Graham Bell applies for a patent for the telephone
1895 – The Importance of Being Earnest, first produced at the St James’s Theatre, London
1918 – Russia finally adopts the Gregorian calendar. see my post here.
First Published in February 2023, revised and updated in February 2024, 2025 On This Day added 2026