The Solstice and the East Pediment of the Parthenon

At the Summer Solstice, I took a group to the British Museum and, a few days later, to Stonehenge, and managed to ‘integrate’ the two into a solstice narrative. At the BM, over years of trying to explain the sculptures, I have been building in my mind an interpretation of the Pediment that gives, I hope, an original insight into the possible intentions of the sculptors. I don’t know how ‘true’ it is, but I do think it gives an insight into metaphor and symbolism in great works of art. Bear in mind that there is a lot of uncertainty about some of the attributions, and, that the male and female virtues that I am talking about are traditional ones, not necessarily how we would express it in the modern world.
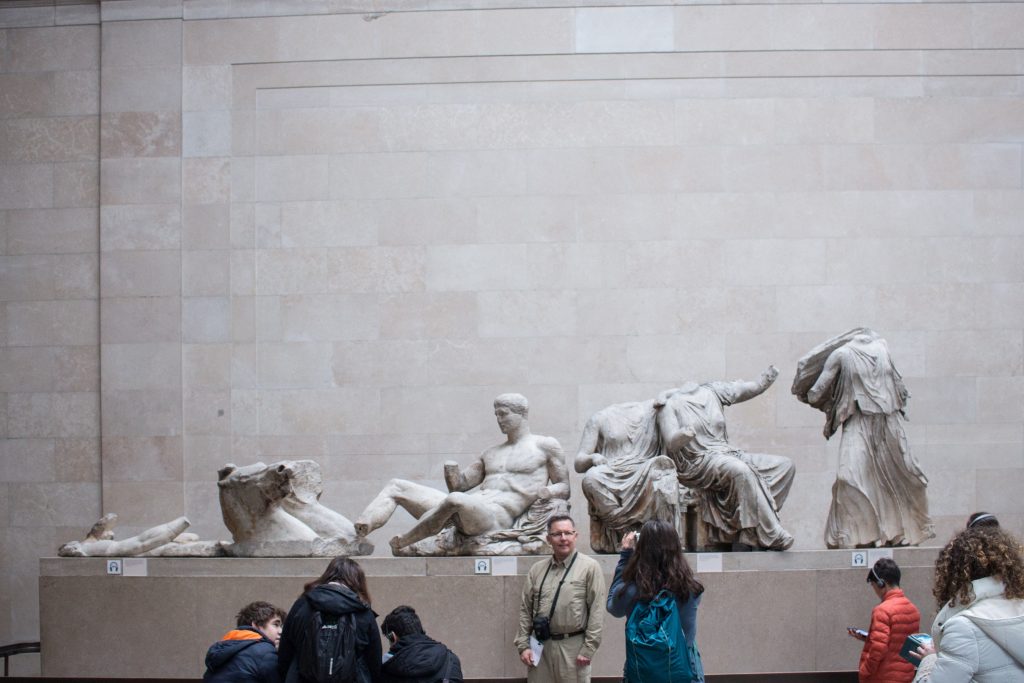

At the left of the above photography, you see the horses that take Helios chariot into the sky to bring up the sun to light the world every day. Most sun deities are male, and the Sun gives light and life to the world, without it this earth is an inert block of ice cold stone. The next statue is casually laying back and looking fit, relaxed and not looking as if he is in that position because of the impossible triangular Pediment space he inhabits. He is the epitome of male strength, usually identified with Hercules but other people have other ideas and a young Dionysus is another suggestion. Whoever he is he represents male beauty and strength. So this end of the pediment represents the Sun and male virtues. This is the East Pediment of the Parthenon which is orientated to the rising sun, a little north of east.
Next figure is Demeter, the goddess of fertility, the goddess of the earth. Placed here to remind us that the Sun needs the Earth to create life and sustenance. It reminds us that the universe is not male, the male only works in conjunction with the female. Demeter is cuddling her daughter Persephone, the Goddess of Hades. She reminds us that life is a cycle of death and life. Plants die, turn into soil and create the conditions for future life.
Next is Hebe, daughter of Zeus and Hera, wife of Heracles (Hercules). She is the cupbearer to the Gods and gives them the ambrosia that keeps them forever young. She is the Goddess of Immortality, a reminder that the universe is eternal.
Next to Hebe is a void where there was the central statue of the east pediment depicting the Birth of Athena (according to Pausanias who wrote a guide in the 2nd Century BC to the Temple). Athena was born from the head of her father Zeus- a virgin birth. Athena therefore is, in some ways, the greatest of the Olympians, as she has the virtues of her female sex and the virtues of her father’s masculinity (and, dear Gods, hopefully not the massive ‘Me Too’ vices of her father). She is therefore, wise, nurturing, just, intuitive, decisive, a leader; an ideal combination of male and female.

Her back story is that her dad, Zeus eats her mum, Metis, who is pregnant with her. Sometime later, he has a cracking headache. Hephaestus, the disabled artificer God hits Zeus over the head with an axe to clear the headache. Zeus gives birth to a fully formed Athena through the split in his head. She was known as Athena Parthenos, Athena the Virgin. Her name is originally Athene but it got changed to Athena in 500 BC.

To Athene’s left is Hestia (Vesta for the Romans). Her name means “hearth, fireplace, altar” and she is the goddess of the domestic sphere, of the comforts of home, of a warm fire enjoyed by a loving family.
The next set are two beautifully draped women languidly leaning on each other, and these are Dione, with her daughter Aphrodite – the Goddess of Love. Dione is the daughter of Gaia and Uranus daughter of earth and sky. So, here, counterpoised to Hercules, are epitomes of women. Women of power, creation, and love.
Finally, we have the exhausted horse of Selene. Her chariot takes the moon into the sky, positioned opposite to Helios and the Sun. Selene is the Moon goddess, and the Moon is beautiful, powerful as it gives us the tides and fundamental to the life of humans as she presides over the menstrual cycle. Compared to the movements of the Sun which any fool can work out, and which are relentless (symbolising Justice) the movements of the Moon are mysterious to most of us. So Selene is beautiful, powerful, creative and the Goddess of Intuition.
So, if you put it all together, the East Pediment of the Parthenon shows that the world is a union of the male and the female, balanced between the two with Zeus and Athene in the middle, with Athene holding the main part because she, in her person, represents both the male and the female.
Of course, we know that the Athenian society was a patriarchal one with women mostly kept in the domestic sphere. But here, at least, women were given an equal billing in the organisation of the Cosmos.
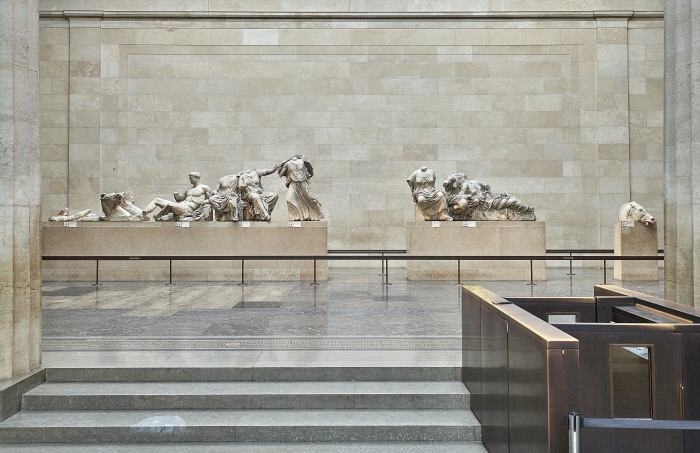

I must end by warning the reader that this is only my interpretation. I am not a scholar of Ancient Greece. I have come to my own conclusion based on spending a lot of time looking at the marbles, doing Solstice Virtual Tours, and mostly informed by the labels in the gallery, with of course, some reading including Mary Beard’s book entitled ‘Parthenon’ and the BM’s guidebook. In particular, I have not incorporated into my ‘story’ the sculptures that were in the gaps that do not survive or only in fragments scattered throughout the Museum world. However, what we do know is that in the centre is Zeus and Athene and at the edges are the chariots of the Sun and the Moon. And so fitting to celebrate the Solstice.
For a look at the Winter Solstice in general, look at my post here:
Originally written in 2022 and revised 2024, 2025