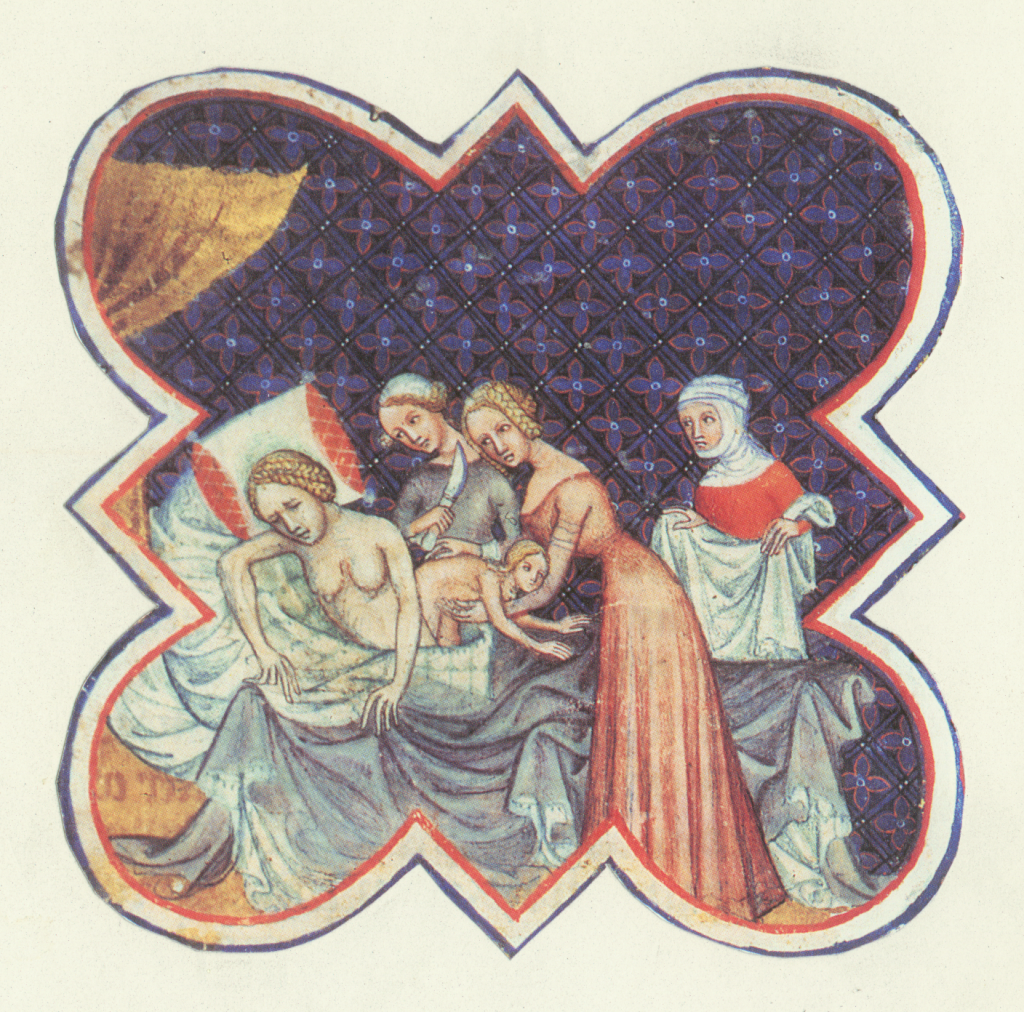
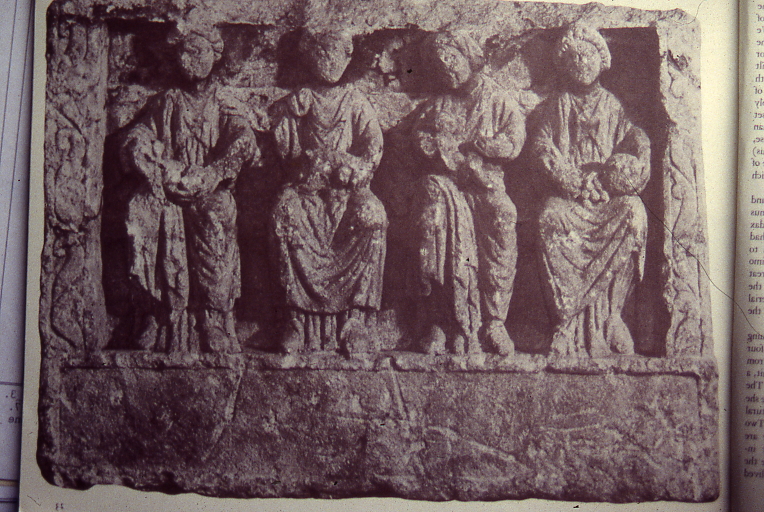
The 15th Century French illustration, above, shows February as a time to cut firewood, dress warmly and stay by the fire. Food on the table is a nutritious pie and the fish are there to remind us it is the month of Pisces. In the other roundel is the other February star sign the Water Carrier, Aquarius.


The poem above is a reference to the Candlemas celebration of the presentation of the child Jesus at the Temple. The paragraph below the line (above) gives a summary of February. It ends with the idea that runs through the Kalendar. There are twelve apostles, twelve days of Christmas, twelve months in the year. So, there are twelve blocks of six years in a person’s allotted 72 years of life. In the January entry the Kalendar suggests the essential uselessness of 0-6 year old children. But for February, it allows that 6-12 years old children are beginning to ‘serve and learn’.
The Kalendar’s View of February

Below, is the text for February. This gives a rural view of life in winter. It ends with the line that February:
‘is the poor man’s pick-purse, the miser’s cut-throat, the enemy to pleasure and the time of patience.’

About the Kalendar of Shepherds.
The Kalendar was printed in 1493 in Paris and provided ‘Devices for the 12 Months.’ The version I’m using is a modern (1908) reconstruction of it. It uses wood cuts from the original 15th Century version and adds various texts from 16th and 17th Century sources. (Couplets by Tusser ‘Five Hundred Parts of Good Husbandrie 1599. Text descriptions of the month from Nicholas Breton’s ‘Fantasticks of 1626.) This provides an interesting view of what was going on in the countryside every month.
For more on the Kalendar look at my post here.
The original Kalendar can be read here: https://wellcomecollection.org/works/f4824s6t
Hesiod and February
Hesiod, in his ‘Works and Days’ describes February as a merciless cold, windy time. Hesiod was writing around 700BC. He gave us ‘the story of Prometheus and Pandora, and the so-called Myth of Five Ages.’ (Links are to Wikipedia.)
Avoid the month Lenaeon, (February) wretched days, all of them fit to skin an ox, and the frosts which are cruel when Boreas blows over the earth.
He blows across horse-breeding Thrace upon the wide sea and stirs it up, while earth and the forest howl.
On many a high-leafed oak and thick pine he falls and brings them to the bounteous earth in mountain glens: then all the immense wood roars and the beasts shudder and put their tails between their legs, even those whose hide is covered with fur; for with his bitter blast he blows even through them, although they are shaggy-breasted.
He goes even through an ox’s hide; it does not stop him. Also he blows through the goat’s fine hair.
But through the fleeces of sheep because their wool is abundant, the keen wind Boreas pierces not at all; but it makes the old man curved as a wheel.
And it does not blow through the tender maiden who stays indoors with her dear mother, unlearned as yet in the works of golden Aphrodite, and who washes her soft body and anoints herself with oil and lies down in an inner room within the house,
on a winter’s day when the Boneless One (an Octopus or a cuttle?) gnaws his foot in his fireless house and wretched home; for the sun shows him no pastures to make for, but goes to and fro over the land and city of dusky men, and shines more sluggishly upon the whole race of the Hellenes.
Then the horned and unhorned denizens of the wood,] with teeth chattering pitifully, flee through the copses and glades, and all, as they seek shelter, have this one care, to gain thick coverts or some hollow rock.
Then, like the Three-legged One (an old man with a stick) whose back is broken and whose head looks down upon the ground, like him, I say, they wander to escape the white snow.
Original text available here. and for more on Hesiod see my post here.
Februarius
The Roman month Februarius was the month of purification. Februa was the name of the purification ritual held on February 15 (full moon) in the old lunar Roman calendar. The Romans originally considered winter a monthless period of the year. So they only had 10 months to the year. Later they added January and February. March was the first month, so September was the 7th month, October the 8th, November 9th and December the 10th and final month. Names derived from the Latin for 7th, 8th, 9th, 10th.
For more on the Roman Calendar look at my posts
https://chr.org.uk/anddidthosefeet/march-1st-the-month-of-new-life/
https://chr.org.uk/anddidthosefeet/leap-day-february-29th/
First Published February 4th 2024, revised 2025, 2026