So I arrived at the hotel in Brussels. Got their free map and looked for likely Wall circuits.
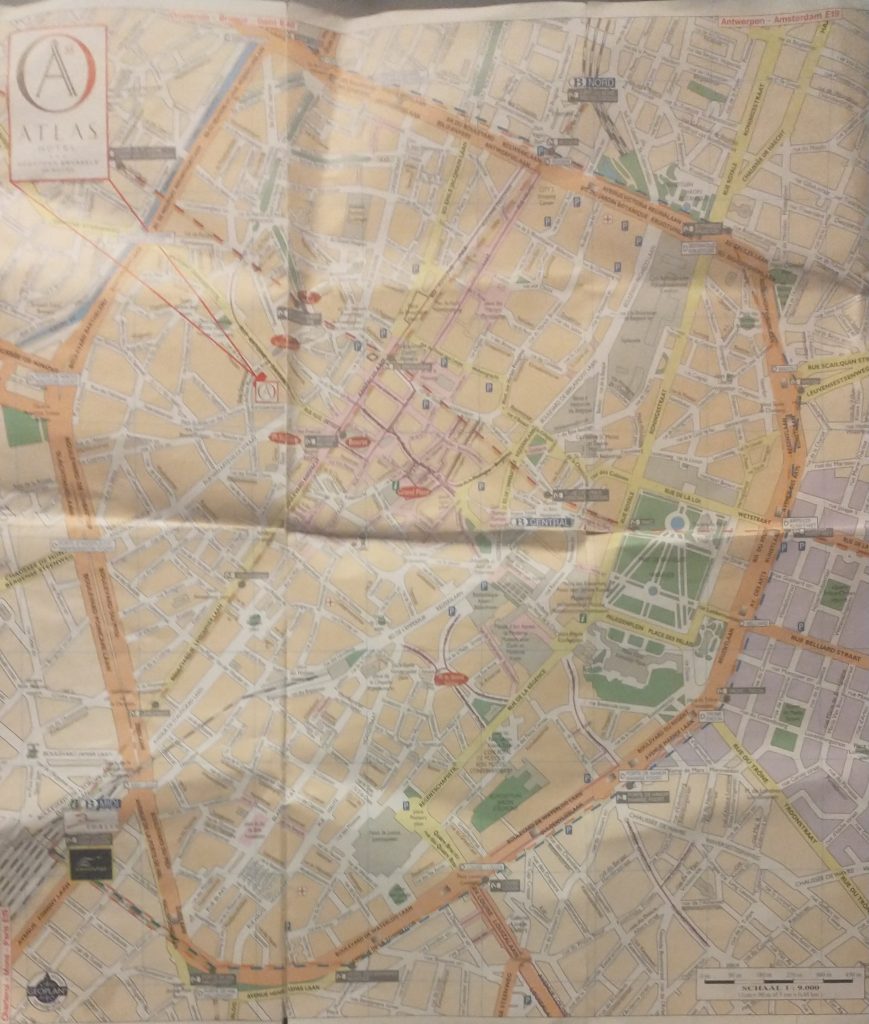
As you will see there is an extensive inner ring road or boulevard clearly marked in orange. This is, I thought probably the Renaissance wall alignment when the town had expanded and the old walls became useless in the face of cannons.
A closer look at the map confirms it was a wall circuit as at junctions there is a grey label saying ‘Porte de Flandres’ or similar.
So the next task is to find if there was an earlier wall circuit on the map. I’m basically looking for curved roads that were originally just inside the walls or just outside.
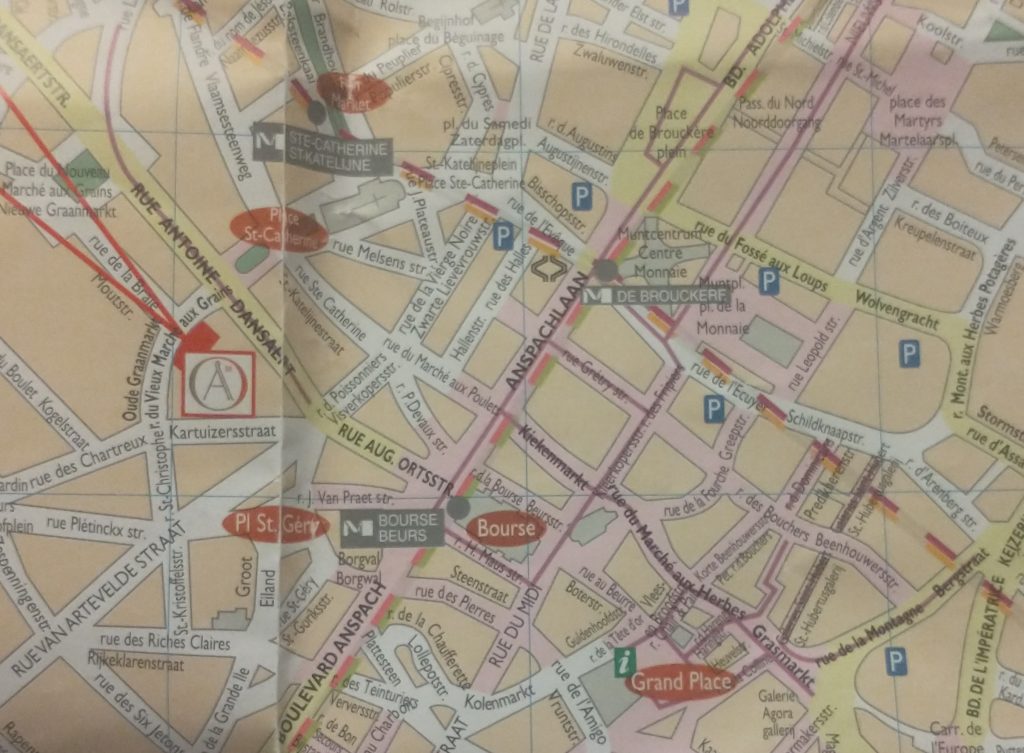
The two red lines coming from the top left point to a red rectangle which is my hotel and by chance is on a curved road which is my guess to be the early wall circuit. It is called the ‘Vieux Marché aux Grains’. I had a quick explore before retiring for the night. But found nothing conclusive and St Catherine’s Church is astride it.
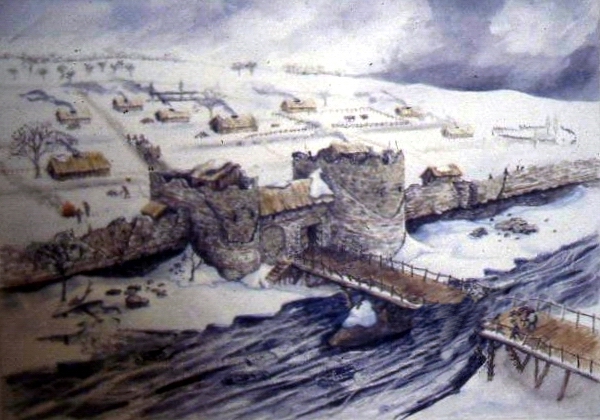
At breakfast, in the basement I failed to notice that 3 of the 4 walls were ancient stone, and there was a picture of a wall and bastion tower. These were pointed out by a staff member, and they suggested they were part of the wall.
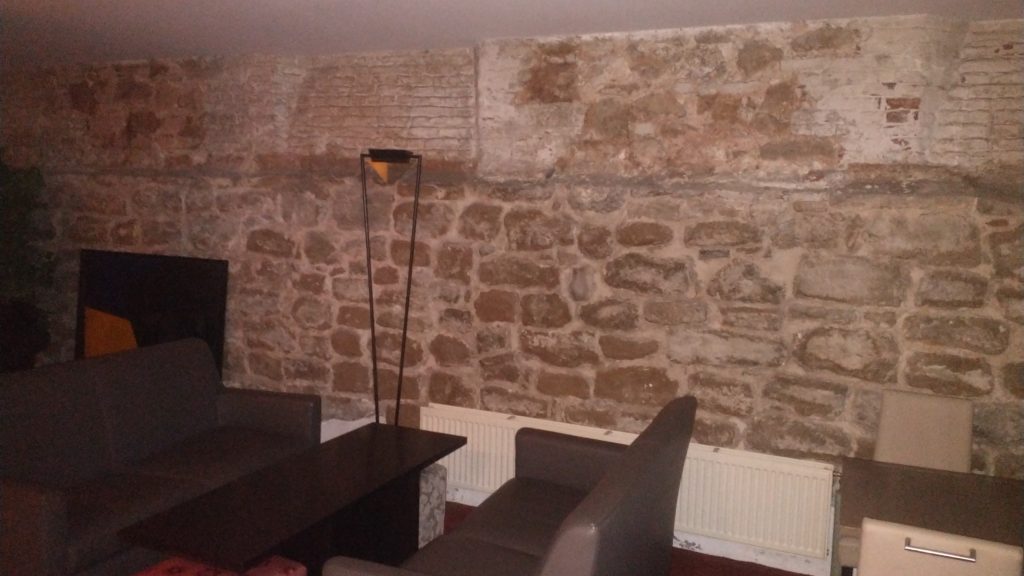

The walls in the basement formed three sides of a rectangle so I had my doubts whether it was ‘the wall’ but it could be a tower or a building built up against the wall. But the picture certainly confirmed my guess that this curved street marked the route of the early wall.

So next I walked up to the ‘Porte de Flandres’ in the north east of the town on what I am calling the Renaissance circuit. I wanted to see if any gate or wall survived (no) and to look at the canal which runs alongside the wall.
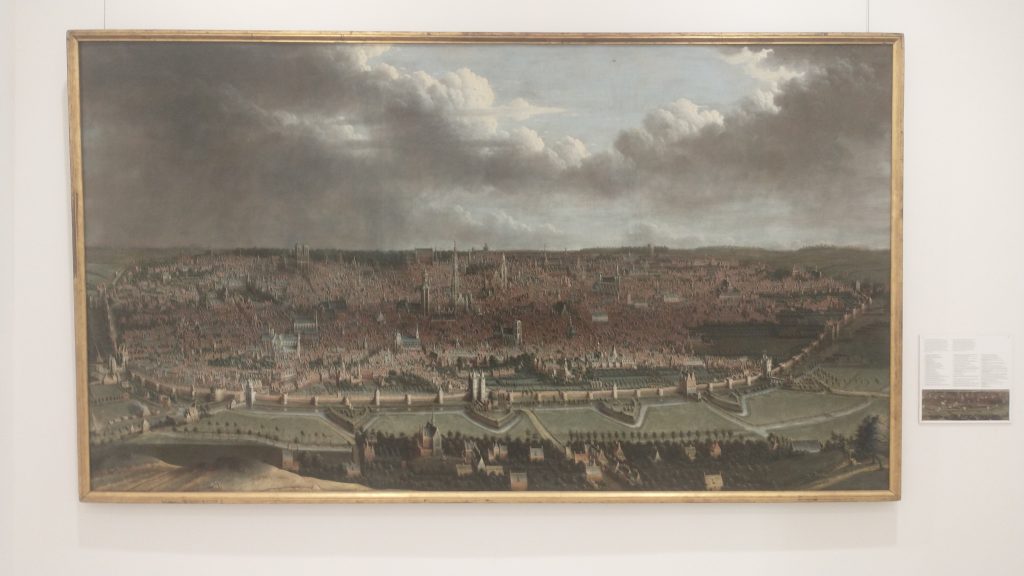
Then to visit Brussels amazing museums where in the Old Masters museum was found the view of the walls that you will find above. The view is from the north east and at the bottom you will see the canal that linked Brussels to the main trade routes with triangular ramparts in front designed to withstand cannon fire, with the canal and the wall behind. Right in the centre of the bottom is the Porte de Flandres. It looks 15th Century to me, give or take a century but the triangular ramparts look 17th Century.
At the Museum were leaflets to a Porte de Halle museum, So I went from the Musee d’Arte et D’ Histoire, through the European Parliament to the old Wall circuit past several old gates which no longer exist and then saw the view below of the Porte de Halle.
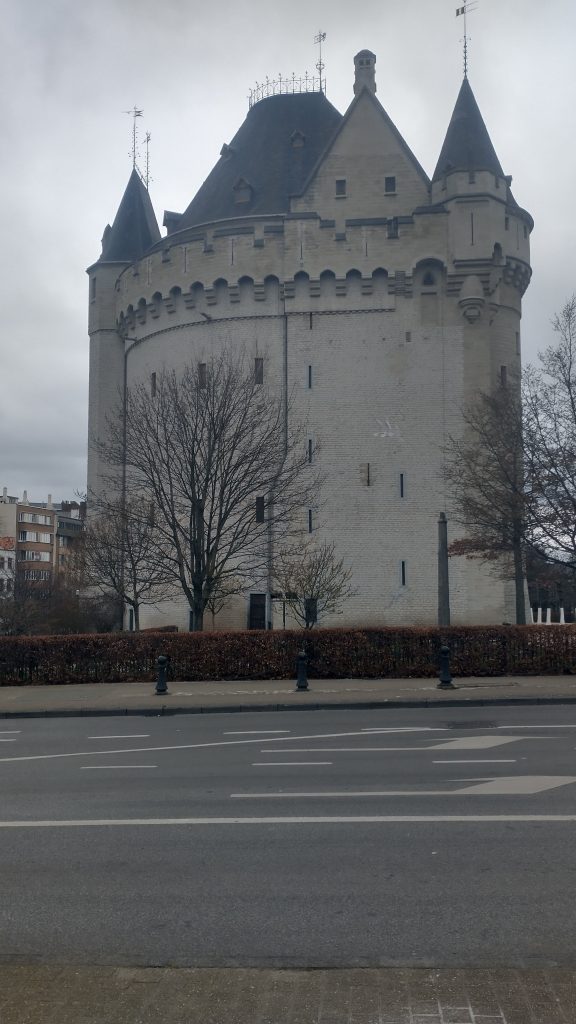

It looks like something from the Très Riches Heures du Duc de Berry which is early 15th Century. I couldn’t confirm because the gatekeeper of the Porte refused entry as, he said, last entry was at 4pm (1 arrived at 4.03pm) although the leaflet clearly says last entry is 45 mins prior to closing at 5pm.
So I went to confirm the existence of the earlier wall circuit. And I will post about that later.