Spring & March
This is the beginning of Spring, meteorologically speaking. There is nothing magical about this day that makes it in any sense actually the start of Spring. It is a convenience determined by meteorologists. They divide the year up into 4 blocks of three months based on average temperature, and the convenience of keeping statistics to months. It could be that spring starts on 2nd March. 14th February. Or the 1st of February as the Celts favoured.
The Venerable Bede in his ‘The Reckoning of Time’, written in 725 AD, quotes more diversity of dates:
However, different people place the beginnings of the seasons at
different times. Bishop Isidore the Spaniard said …, spring [starts] on the 8th kalends of
March [22 February],…
But the Greeks and Romans, whose authority on these matters, rather than that of the
Spaniards, it is generally preferable to follow, deem that spring [begins] on the 7th ides of February [7 February],…
Noting that summer and winter begin with
the evening or morning rising and setting of the Pleiades, they place the
commencement of spring and autumn when the Pleiades rise and set
around the middle of the night.
There is nothing that says we have to have 4 seasons. Egypt had three seasons, the tropics have two. Celts divided the year into 8. Plants have been blooming, sprouting and budding since January, and some will wait until later in the year. Lambs have been born since January. But scientists and society find it easiest to keep statistics on a monthly basis so March 1st it is.
Astronomically, the seasons are more rationally divided by the movement of the Sun. So Spring begins on the spring or vernal equinox, 20th or 21st of March. For my Spring Equinox post go here.
Anglo-Saxon March
In Anglo-Saxon ‘Hrethamonath’ is the month of the Goddess Hretha. Bede gives no further information on who she was and nothing else is known about her. Her name is Latinised to Rheda. J R. R. Tolkein used the Anglo-Saxon calendar as the calendar for the Shire where the third month is called Rethe.
For the Anglo-Saxon, spring was looked forward to with great joy after the bleakness of winter. Christian Anglo-Saxons also saw this as the pivotal month in the year. It was in March that the world was created, and the Messiah conceived, revealed, executed, and ascended to heaven. See my post:
In Welsh the month is called Mawrth, (derived it is thought from the Latin Martius). Gaelic Mart or Earrach Geamraidth – which means the ‘winter spring’.
Medieval/Early Modern March
The illustration (above), from the Kalendar of Shepherds, shows that in Pisces and early Ares preparation was still the main order of the farming day, clearing out the moats, and preparing the fruit trees. Lambing is also increasing in number. And the early modern text below from the Kalendar gives a fine description of the joys of spring.


For more details of the Kalendar of Shepherds look at my post on December.
Roman March
March the 1st was the beginning of the Roman year in Rome’s early days. The Month was named after Mars, the God of War, as Mars was the patron God of the Rome. March was also the beginning of the campaign season, and the army was prepared, and ceremonies held to Mars. The Salii, twelve youths dressed in archaic fighting costumes led a procession singing the Carmen Saliare. March 1 was also the Matronalia a festival celebrating childbirth motherhood. Dedicated to the Mother Juno Lucina,
Ovid & March & Kalends, Nones & Ides
Ovid says the year started on the Kalends of March. Here is what Britannica says about their strange system of dividing months:
‘In a 31-day month such as March, the Kalends was day 1, with days 2–6 being counted as simply “before the Nones.” The Nones fell on day 7, with days 8–14 “before the Ides” and the 15th as the Ides. After this the days were counted as “before the Kalends” of the next month’.
More about this if you read my post on the Ides of March and Julius Caesar.
At the beginning of his book, Fasti, Ovid provides the story of Rome’s foundation. Mars took Silvia the Vestal while she slept. She later gave birth to Romulus and Remus. He also gives details of how Rome was organised. In the piece of the long text I have chosen below he discusses Romulus’ arrangement of the year. It is a year that began on the 1st March, and had only 10 months. 10 is the number of digits we have and the length of pregnancy (so Ovid says).
Ovid wrote in his almanac poem the Fasti:
So, untaught and lacking in science, each five-year lustre
That they calculated was short by two whole months.
A year was when the moon returned to full for the tenth
time:
And that was a number that was held in high honour:
Because it’s the number of fingers we usually count with,
Or because a woman produces in ten months,
Or because the numerals ascend from one to ten,
And from that point we begin a fresh interval.
So Romulus divided the hundred Senators into ten groups,
And instituted ten companies of men with spears,
And as many front-rank and javelin men,
And also those who officially merited horses.
He even divided the tribes the same way, the Titienses,
The Ramnes, as they are called, and the Luceres.
And so he reserved the same number for his year,
It ís the time for which the sad widow mourns her man.
If you doubt that the Kalends of March began the year,
You can refer to the following evidence.
The priest’s laurel branch that remained all year,
Was removed then, and fresh leaves honoured.
Then the king’s door is green with Phoebus’ bough,
Set there, and at your doors too, ancient wards.
And the withered laurel is taken from the Trojan hearth,
So Vesta may be brightly dressed with new leaves.
Also, it’s said, a new fire is lit at her secret shrine,
And the rekindled flame acquires new strength.
And to me it’s no less a sign that past years began so,
That in this month worship of Anna Perenna begins.
Then too it’s recorded public offices commenced,
Until the time of your wars, faithless Carthaginian.
Lastly Quintilis is the fifth (TXLQWXV) month from March,
And begins those that take their names from numerals.
Numa Pompilius, led to Rome from the lands of olives,
Was the first to realise the year lacked two months,
Learning it from Pythagoras of Samos, who believed
We could be reborn, or was taught it by his own Egeria.
But the calendar was still erratic down to the time
When Caesar took it, and many other things, in hand.
That god, the founder of a mighty house, did not
Regard the matter as beneath his attention,
And wished to have prescience of those heavens
Promised him, not be an unknown god entering a strange
house.
He is said to have drawn up an exact table
Of the periods in which the sun returns to its previous
signs.
He added sixty-five days to three hundred,
And then added a fifth part of a whole day.
That’s the measure of the year: one day
The sum of the five part-days is added to each lustre.
Translated by A. S. Kline online here:
For much more about the Roman Year (and leap years) look at my post here.
On This Day
St David’s Day – It is also the Feast of St David, (or Dewi) the patron saint of Wales, who lived in the sixth century AD. Little that is known about him is contemporary but he was an abbot-bishop. His hagiography was written in the 11th Century and not very trustworthy, but the aim was to show the independence of the Welsh Church from Canterbury. His association with the leek is unexplained.
293 – Inauguration of the Tetrarchy
Diocletian reorganises the Roman Empire to be a Tetrarchy with himself and Maximian the Augusti, one in the East the other in the West. Below them were Constantius Chlorus and Galerius the Caesars.
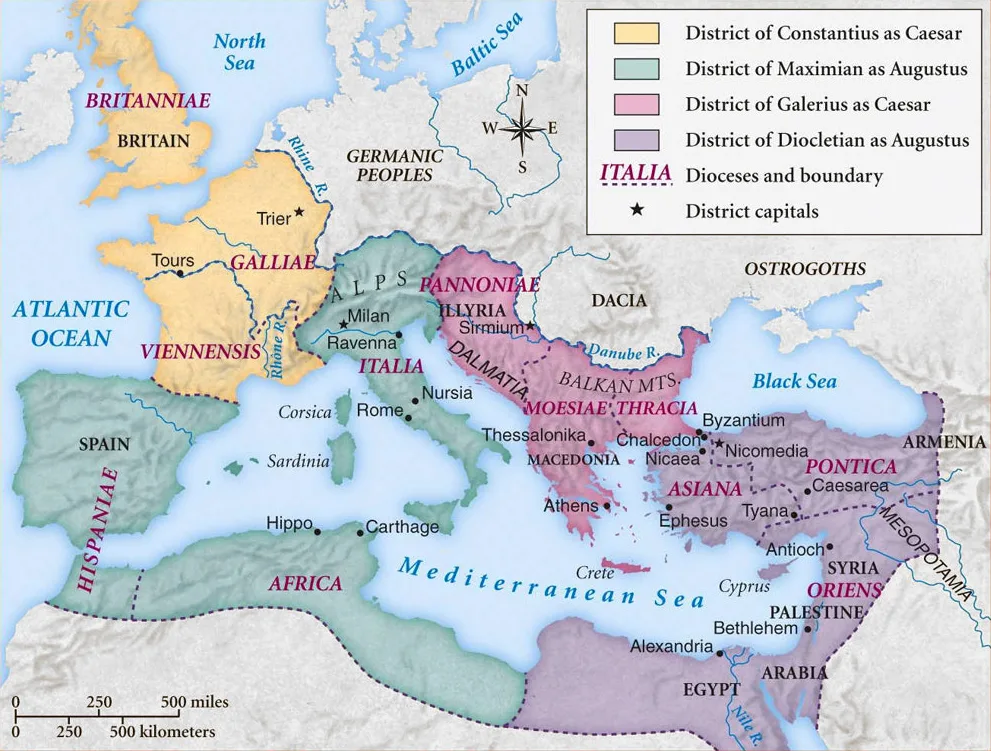
Below them were Prefectures run by Prefects, who controlled officials called the Vicarious. Britannia, was a Diocese ruled by the Vicarious in London. The Diocese was divided into 4 Provinces,. In charge of those were the Governors, who were now civilians rather than military figures.
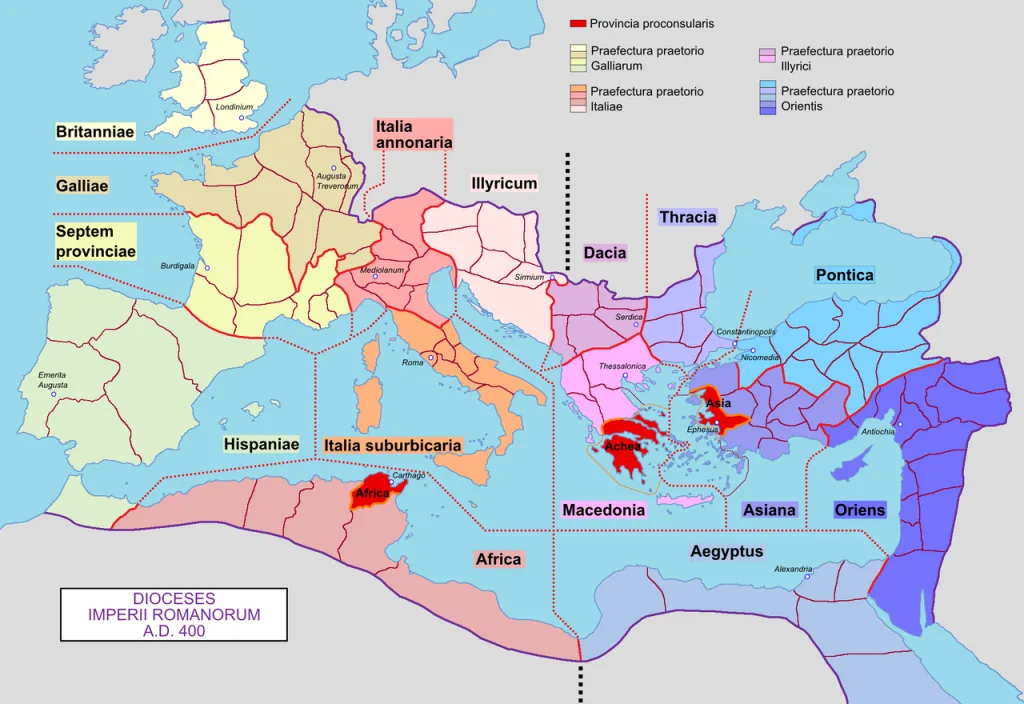
The reorganisation was designed to provide a peaceful career path for ambitious men, but in that it failed.
1562 – Massacre in Wassy France, when sixty-three Huguenots were killed and the French Wars of Religion began. Many Huguenots came to Britain, and many settled in Spitalfields, London. My family believe we are Huguenots from the East End.
1628 – Charles I decrees that the ship tax should be extended to every county. This was not put to a Parliament, and illegal impositions like this eventually lead to the English Civil War in 1642. (see my post on the beginning of the Civil War here:
First Published in 2024, and revised in 2025