Rood is another word for the Cross. Parish Churches used to have a Rood Screen separating the holy Choir from the more secular Nave. This screen was topped with a statue of the Crucified Jesus nailed to a Rood. Sp Roodmas, is the festival of the Holy Cross.
Roodmas is celebrated on May 3rd and September 14th, although the Church of England aligned has itself with the Catholic Church’s main celebration on September 14th.
Roodmas and the True Cross
The two dates of Roodmas reflects that it commemorates two events:
The first was the discovery of the Holy Cross in Jerusalem in September 14th 326 by Queen Helena. She was the wife of Constantius Chlorus, Augustus and mother of Constantine the Great. In Jerusalem, Queen Helena found the Cross with the nails, and the crown of thorns.
How did she know she had found the true cross? She placed the timber in contact with a deathly sick woman who was revived by it. So, they thought it was the touch of the True Cross. She had most of the Cross sent back to Constantinople in the care of her son, Constantine the Great.
The part of the Holy Cross that was left behind in Jerusalem was taken by the Persians. But it was recovered by the Byzantine Emperor Heraclius in May 3rd 628 in a peace treaty.
See my post on September 14th here.
Shivered into fragments
Over the years, the Cross was shivered into ever smaller pieces. Fragments were sent to Emperors, Kings, Queens, Dukes, Counts, Popes, Bishops, Abbots, and Abbesses. They swapped relics with each other. The fragments were cased in beautiful reliquaries. And were venerated for those of faith and helped those who could be helped by healing by faith.
King Charles III and the True Cross
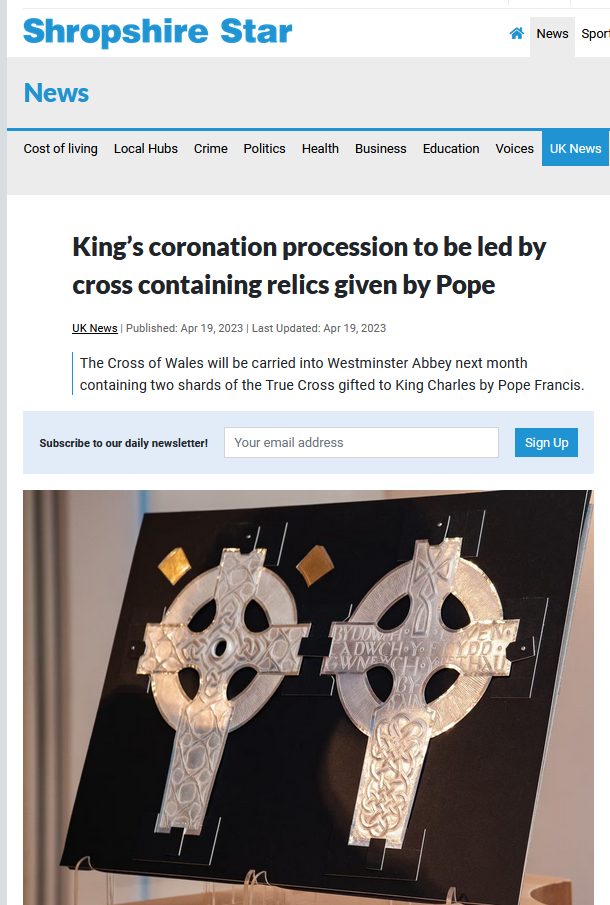
The Shropshire News reported that two pieces of the True Cross were given to Charles III by the Pope! They have been put into a cross called the Welsh Cross. This was part of the Coronation Procession. The King gave the Cross (I assume with the pieces of the Holy Cross) to the Church in Wales. Let the Shropshire News tell the story:

This is quite extraordinarily medieval, and fits in with the news that we were encouraged to take an oath of allegiance to the new King.
I, (Insert full name), do swear that I will be faithful and bear true allegiance to His Majesty King Charles, his heirs and successors, according to law. So help me God.
It is a clear reminder that we are subjects not citizens and news, as a nation, we still set store by superstitions.
The Duke of Buckingham and the True Cross
The Duke of Buckingham had a piece in his collection, which he kept at York House in the early 17th Century. How he got it, I don’t know. But I think he must have acquired it from the aftermath of the destruction of the Reformation. John Tradescant, who looked after the Duke’s collection until Buckingham was murdered, had a piece of the True Cross. Tradecant created Britain’s first Museum, Tradescant’s Ark. Again, I suspect (without any evidence) that he got the fragments from Buckingham. Did he acquire it after the murder? Or shiver off a timber fragment hoping no one would notice?
Guild of the Holy Cross Stratford
The Chapel that Shakespeare’s Father controlled as Bailiff of Stratford on Avon, was dedicated to the Legend of the True Cross, to find out more read my post on September 14th here:
First Written on May 3rd 2023, revised May 3rd 2024, and 2025